Evaluation of renal markers in systemic autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 37352246
- PMCID: PMC10289317
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278441
Evaluation of renal markers in systemic autoimmune diseases
Abstract
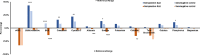
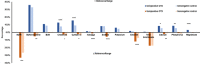
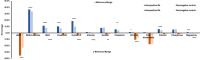
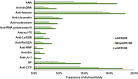
Renal involvement is a common occurrence in subjects with systemic autoimmune diseases. The renal manifestation and its severity depend on the underlying condition and may reversely complicate the clinical course of autoimmune diseases. Renal function markers have been widely used in the assessment of normal functioning of kidneys including glomerular filtration rate and concentrating and diluting capacity of the kidney. An increase or decrease in the values of these markers may indicate kidney dysfunction. In this study, a number of critical renal markers were examined in seropositive autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), connective tissue disorder (CTD), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The data from three cohorts of subjects enrolled in renal markers and autoimmune antibody testing between January 2015 to August 2019 were retrospectively studied. The prevalence of renal markers that were out of the reference range and their average levels in female and male subgroups across SLE, CTD, and RA cohorts were compared and analyzed. The levels of renal markers are significantly affected by the presence of autoantibodies, in particular eGFR, cystatin C, and albumin. Autoantibodies were also more frequent in subjects with severe renal function damage. Close follow-up of both renal markers and autoantibodies may potentially assist in the early diagnosis of kidney diseases and improve the survival and life expectancy of autoimmune patients.
Copyright: © 2023 Krishnamurthy et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: YY and QS are paid employees of Vibrant America LLC. KK, VJ, TW, KB, HK, JJR, are paid employees of Vibrant Sciences LLC. Vibrant Sciences or Vibrant America could benefit from increased testing based on the results. There are no patents, products in development, or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brief Report: How Do Patients With Newly Diagnosed Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Present? A Multicenter Cohort of Early Systemic Lupus Erythematosus to Inform the Development of New Classification Criteria.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Jan;71(1):91-98. doi: 10.1002/art.40674. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30035365
-
Autoantibodies persist in relatives to systemic lupus erythematosus patients during 12 years follow-up.Lupus. 2017 Jun;26(7):723-728. doi: 10.1177/0961203316676378. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Lupus. 2017. PMID: 27831535
-
An updated advance of autoantibodies in autoimmune diseases.Autoimmun Rev. 2021 Feb;20(2):102743. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102743. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Autoimmun Rev. 2021. PMID: 33333232 Review.
-
Presence of antinucleosome autoantibodies in a restricted set of connective tissue diseases: antinucleosome antibodies of the IgG3 subclass are markers of renal pathogenicity in systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):76-84. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<76::AID-ANR10>3.0.CO;2-I. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. PMID: 10643702
-
[Autoantibodies to the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins and the autoimmune diseases].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 1999 Aug;21(4):311-4. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 1999. PMID: 12567457 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Kidney Biopsy and Immuno-Rheumatological Diseases: A Retrospective and Observational Study.J Pers Med. 2024 Jan 13;14(1):92. doi: 10.3390/jpm14010092. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38248794 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of 3-O-sulfotransferase enzymes, Hs3st3a1 and Hs3st3b1, reduces kidney and glomerular size and disrupts glomerular architecture.Matrix Biol. 2024 Nov;133:134-149. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2024.06.006. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Matrix Biol. 2024. PMID: 38944161
-
Prediction of Lupus Classification Criteria via Generative AI Medical Record Profiling.BioTech (Basel). 2025 Mar 6;14(1):15. doi: 10.3390/biotech14010015. BioTech (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227336 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

