Dermatologic complications in transplantation and cellular therapy for acute leukemia
- PMID: 37353285
- PMCID: PMC10291442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.beha.2023.101464
Dermatologic complications in transplantation and cellular therapy for acute leukemia
Abstract
Adoptive cellular immunotherapy, mainly hematopoietic stem cell transplant and CAR-T cell therapy have revolutionized treatment of patients with acute leukemia. Indications and inclusion criteria for these treatments have expanded in recent years. While these therapies are associated with significant improvements in disease response and overall survival, patients may experience adverse events from associated chemotherapy conditioning, engraftment, cytokine storm, supportive medications, and post-transplant maintenance targeted therapies. Supportive oncodermatology is a growing specialty to manage cutaneous toxicities resulting from the anti-cancer therapies. In this review, we summarize diagnosis and management of the common cutaneous adverse events including drug eruptions, graft-versus-host disease, neoplastic and paraneoplastic complications in patients undergoing cellular therapies.
Keywords: CAR-T cell therapy; Dermatological complications; Drug eruptions; GVHD; Hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
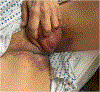
- Bolognia JL, Cooper DL, Glusac EJ. Toxic erythema of chemotherapy: a useful clinical term. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:524–9. - PubMed
-
- Wolf R, Tüzün Y. Baboon syndrome and toxic erythema of chemotherapy: Fold (intertriginous) dermatoses. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:462–5. - PubMed
-
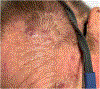
- Hunjan MK, Nowsheen S, Ramos-Rodriguez AJ, Hashmi SK, Bridges AG, Lehman JS, et al. Clinical and histopathological spectrum of toxic erythema of chemotherapy in patients who have undergone allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019;12:19–25. - PubMed
-
- Mehta H, Mete UK, Gupta P, Ranjan KR, Nahar Saikia U, Mahajan R. Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like presentation of toxic erythema of chemotherapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:1201–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

