NFIC regulates ribosomal biology and ER stress in pancreatic acinar cells and restrains PDAC initiation
- PMID: 37353485
- PMCID: PMC10290102
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39291-x
NFIC regulates ribosomal biology and ER stress in pancreatic acinar cells and restrains PDAC initiation
Abstract
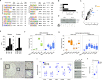
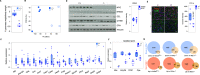
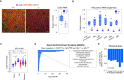
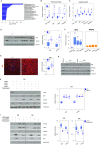
Pancreatic acinar cells rely on PTF1 and other transcription factors to deploy their transcriptional program. We identify NFIC as a NR5A2 interactor and regulator of acinar differentiation. NFIC binding sites are enriched in NR5A2 ChIP-Sequencing peaks. Nfic knockout mice have a smaller, histologically normal, pancreas with reduced acinar gene expression. NFIC binds and regulates the promoters of acinar genes and those involved in RNA/protein metabolism, and Nfic knockout pancreata show defective ribosomal RNA maturation. NFIC dampens the endoplasmic reticulum stress program through binding to gene promoters and is required for resolution of Tunicamycin-mediated stress. NFIC is down-regulated during caerulein pancreatitis and is required for recovery after damage. Normal human pancreata with low levels of NFIC transcripts display reduced expression of genes down-regulated in Nfic knockout mice. NFIC expression is down-regulated in mouse and human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Consistently, Nfic knockout mice develop a higher number of mutant Kras-driven pre-neoplastic lesions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oncogenic KRAS Reduces Expression of FGF21 in Acinar Cells to Promote Pancreatic Tumorigenesis in Mice on a High-Fat Diet.Gastroenterology. 2019 Nov;157(5):1413-1428.e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.030. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31352001 Free PMC article.
-
GRP78 haploinsufficiency suppresses acinar-to-ductal metaplasia, signaling, and mutant Kras-driven pancreatic tumorigenesis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 May 16;114(20):E4020-E4029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616060114. Epub 2017 May 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28461470 Free PMC article.
-
miR-802 Suppresses Acinar-to-Ductal Reprogramming During Early Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Carcinogenesis.Gastroenterology. 2022 Jan;162(1):269-284. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.029. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Gastroenterology. 2022. PMID: 34547282
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and acinar cells: a matter of differentiation and development?Gut. 2012 Mar;61(3):449-58. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.235804. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Gut. 2012. PMID: 21730103 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting acinar cell reprogramming in pancreatic cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug 21;22(31):7046-57. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7046. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27610015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment of a chemokine-based prognostic model and identification of CXCL10+ M1 macrophages as predictors of neoadjuvant therapy efficacy in colorectal cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1400722. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1400722. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39170612 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of epithelial-related artificial neural network prognostic models for the prediction of bladder cancer prognosis through comprehensive analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 17;10(15):e34632. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34632. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157397 Free PMC article.
-
ZDHHC20-mediated S-palmitoylation of YTHDF3 stabilizes MYC mRNA to promote pancreatic cancer progression.Nat Commun. 2024 May 31;15(1):4642. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49105-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38821916 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression signatures of individual ductal carcinoma in situ lesions identify processes and biomarkers associated with progression towards invasive ductal carcinoma.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 13;13(1):3399. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30573-4. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35697697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pandol, S. J. The Exocrine Pancreas (Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences, 2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

