Role of liensinine in sensitivity of activated macrophages to ferroptosis and in acute liver injury
- PMID: 37353487
- PMCID: PMC10290152
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-023-01481-3
Role of liensinine in sensitivity of activated macrophages to ferroptosis and in acute liver injury
Abstract
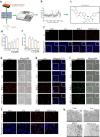
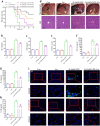
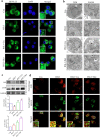
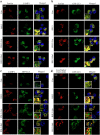
Acute liver injury (ALI) is an acute inflammatory liver disease with a high mortality rate. Alternatively, activated macrophages (AAMs) have been linked to the inflammation and recovery of ALI. However, the mechanism underlying AAM death in ALI has not been studied sufficiently. We used liensinine (Lie) as a drug of choice after screening a library of small-molecule monomers with 1488 compounds from traditional Chinese remedies. In ALI, we evaluated the potential therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms of action of the drug in ALI and found that it effectively inhibited RSL3-induced ferroptosis in AAM. Lie significantly reduced lipid peroxidation in RSL3-generated AAM. It also improved the survival rate of LPS/D-GalN-treated mice, reduced serum transaminase activity, suppressed inflammatory factor production, and may have lowered AAM ferroptosis in ALI. Lie also inhibited ferritinophagy and blocked Fe2+ synthesis. Following combined treatment with RSL3 and Lie, super-resolution microscopy revealed a close correlation between ferritin and LC3-positive vesicles in the AAM. The co-localization of ferritin and LC3 with LAMP1 was significantly reduced. These findings suggest that Lie may ameliorate ALI by inhibiting ferritinophagy and enhancing AMM resistance to ferroptosis by inhibiting autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Therefore, Lie may be used as a potential therapeutic agent for patients with ALI.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
YAP1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 1;13:884362. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.884362. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35979359 Free PMC article.
-
Maresin1 Protect Against Ferroptosis-Induced Liver Injury Through ROS Inhibition and Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 Activation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 4;13:865689. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.865689. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35444546 Free PMC article.
-
Maresin 1 protects against lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting macrophage pyroptosis and inflammatory response.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Jan;195:114863. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114863. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34861244
-
The role of ferroptosis in acute lung injury.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 May;477(5):1453-1461. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04327-7. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35166985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Peroxidation-Dependent Cell Death Regulated by GPx4 and Ferroptosis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;403:143-170. doi: 10.1007/82_2016_508. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28204974 Review.
Cited by
-
Ferroptosis: A key regulator and potential target for tissue injury.Histol Histopathol. 2025 Jun;40(6):813-823. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-838. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Histol Histopathol. 2025. PMID: 39530310 Review.
-
Interaction between macrophages and ferroptosis: Metabolism, function, and diseases.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Mar 5;138(5):509-522. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003189. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 39245648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dimethyl malonate preserves brain and neurobehavioral phenotype following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia by inhibiting FTH1-mediated ferritinophagy.Redox Biol. 2025 Jul 29;86:103792. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103792. Online ahead of print. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40749519 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for Monitoring NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2845:177-189. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4067-8_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39115666
-
Ferroptosis as a key player in the pathogenesis and intervention therapy in liver injury: focusing on drug-induced hepatotoxicity.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 17. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04115-w. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40244448 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

