Systems-level analyses of protein-protein interaction network dysfunctions via epichaperomics identify cancer-specific mechanisms of stress adaptation
- PMID: 37353488
- PMCID: PMC10290137
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39241-7
Systems-level analyses of protein-protein interaction network dysfunctions via epichaperomics identify cancer-specific mechanisms of stress adaptation
Abstract
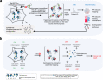
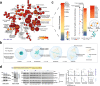
Systems-level assessments of protein-protein interaction (PPI) network dysfunctions are currently out-of-reach because approaches enabling proteome-wide identification, analysis, and modulation of context-specific PPI changes in native (unengineered) cells and tissues are lacking. Herein, we take advantage of chemical binders of maladaptive scaffolding structures termed epichaperomes and develop an epichaperome-based 'omics platform, epichaperomics, to identify PPI alterations in disease. We provide multiple lines of evidence, at both biochemical and functional levels, demonstrating the importance of these probes to identify and study PPI network dysfunctions and provide mechanistically and therapeutically relevant proteome-wide insights. As proof-of-principle, we derive systems-level insight into PPI dysfunctions of cancer cells which enabled the discovery of a context-dependent mechanism by which cancer cells enhance the fitness of mitotic protein networks. Importantly, our systems levels analyses support the use of epichaperome chemical binders as therapeutic strategies aimed at normalizing PPI networks.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center holds the intellectual rights to this portfolio. Samus Therapeutics Inc, of which G.C. has partial ownership, and is a member of its scientific advisory board, has licensed the epichaperome portfolio. G.C., A.R. and T.T. are inventors on the licensed intellectual property. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

