Fast and accurate genome-wide predictions and structural modeling of protein-protein interactions using Galaxy
- PMID: 37353753
- PMCID: PMC10288729
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-023-05389-8
Fast and accurate genome-wide predictions and structural modeling of protein-protein interactions using Galaxy
Abstract
Background: Protein-protein interactions play a crucial role in almost all cellular processes. Identifying interacting proteins reveals insight into living organisms and yields novel drug targets for disease treatment. Here, we present a publicly available, automated pipeline to predict genome-wide protein-protein interactions and produce high-quality multimeric structural models.
Results: Application of our method to the Human and Yeast genomes yield protein-protein interaction networks similar in quality to common experimental methods. We identified and modeled Human proteins likely to interact with the papain-like protease of SARS-CoV2's non-structural protein 3. We also produced models of SARS-CoV2's spike protein (S) interacting with myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein receptor and dipeptidyl peptidase-4.
Conclusions: The presented method is capable of confidently identifying interactions while providing high-quality multimeric structural models for experimental validation. The interactome modeling pipeline is available at usegalaxy.org and usegalaxy.eu.
Keywords: Galaxy workflow; Protein–protein interactions; Structural modeling.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.G., D.B., N.C. and A.N. are founders of and hold equity in GalaxyWorks, LLC. The results of the study discussed in this publication could affect the value of GalaxyWorks, LLC.
Figures


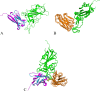
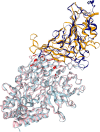

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

