Bempedoic Acid for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Statin-Intolerant Patients
- PMID: 37354546
- PMCID: PMC10336623
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.9696
Bempedoic Acid for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Statin-Intolerant Patients
Abstract
Importance: The effects of bempedoic acid on cardiovascular outcomes in statin-intolerant patients without a prior cardiovascular event (primary prevention) have not been fully described.
Objective: To determine the effects of bempedoic acid on cardiovascular outcomes in primary prevention patients.
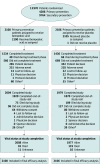
Design, setting, and participants: This masked, randomized clinical trial enrolled 13 970 statin-intolerant patients (enrollment December 2016 to August 2019 at 1250 centers in 32 countries), including 4206 primary prevention patients.
Interventions: Participants were randomized to oral bempedoic acid, 180 mg daily (n = 2100), or matching placebo (n = 2106).
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy measure was the time from randomization to the first occurrence of any component of a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization.
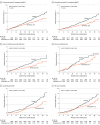
Results: Mean participant age was 68 years, 59% were female, and 66% had diabetes. From a mean baseline of 142.2 mg/dL, compared with placebo, bempedoic acid reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels by 30.2 mg/dL (21.3%) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels by 0.56 mg/L (21.5%), from a median baseline of 2.4 mg/L. Follow-up for a median of 39.9 months was associated with a significant risk reduction for the primary end point (111 events [5.3%] vs 161 events [7.6%]; adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.70 [95% CI, 0.55-0.89]; P = .002) and key secondary end points, including the composite of cardiovascular death, MI, or stroke (83 events [4.0%] vs 134 events [6.4%]; HR, 0.64 [95% CI, 0.48-0.84]; P < .001); MI (29 events [1.4%] vs 47 events [2.2%]; HR, 0.61 [95% CI, 0.39-0.98]); cardiovascular death (37 events [1.8%] vs 65 events [3.1%]; HR, 0.61 [95% CI, 0.41-0.92]); and all-cause mortality (75 events [3.6%] vs 109 events [5.2%]; HR, 0.73 [95% CI, 0.54-0.98]). There was no significant effect on stroke or coronary revascularization. Adverse effects with bempedoic acid included a higher incidence of gout (2.6% vs 2.0%), cholelithiasis (2.5% vs 1.1%), and increases in serum creatinine, uric acid, and hepatic enzyme levels.
Conclusions: In a subgroup of high-risk primary prevention patients, bempedoic acid treatment was associated with reduced major cardiovascular events.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02993406.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Bempedoic Acid for High-Risk Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Not a Statin Substitute but a Good Plan B.JAMA. 2023 Jul 11;330(2):123-125. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.9854. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37354548 No abstract available.
-
Bempedoic Acid for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Events.JAMA. 2023 Nov 7;330(17):1696. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.17335. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37934223 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(10):e177-e232. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

