Is multimodal occupational therapy in addition to usual care cost-effective in people with thumb carpometacarpal osteoarthritis? A cost-utility analysis of a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 37355263
- PMCID: PMC10314563
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-063103
Is multimodal occupational therapy in addition to usual care cost-effective in people with thumb carpometacarpal osteoarthritis? A cost-utility analysis of a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: The aim was to evaluate the cost-utility of a 3-month multimodal occupational therapy intervention in addition to usual care in patients with thumb carpometacarpal osteoarthritis (CMC1 OA).
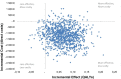
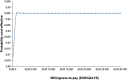
Methods: A cost-utility analysis was performed alongside a multicentre randomised controlled trial including three rheumatology departments in Norway. A total of 180 patients referred to surgical consultation due to CMC1 OA were randomised to either multimodal occupational therapy including patient education, hand exercises, assistive devices and orthoses (n=90), or usual care receiving only information on OA (n=90). The outcome measure was quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) derived from the generic questionnaire EQ-5D-5L over a 2-year period. Resource use and health-related quality of life of the patients were prospectively collected at baseline, 4, 18 and 24 months. Costs were estimated by taking a healthcare and societal perspective. The results were expressed as incremental cost-effectiveness ratios, and a probabilistic sensitivity analysis with 1000 replications following intention-to-treat principle was done to account for uncertainty in the analysis.
Results: During the 2-year follow-up period, patients receiving multimodal occupational therapy gained 0.06 more QALYs than patients receiving usual care. The mean (SD) direct costs were €3227 (3546) in the intervention group and €4378 (5487) in the usual care group, mean difference €-1151 (95% CI -2564, 262). The intervention was the dominant treatment with a probability of 94.5% being cost-effective given the willingness-to-pay threshold of €27 500.
Conclusions: The within-trial analysis demonstrated that the multimodal occupational therapy in addition to usual care was cost-effective at 2 years in patients with CMC1 OA.
Trial registration number: NCT01794754.
Keywords: hand & wrist; health economics; musculoskeletal disorders; rheumatology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Marshall M, Peat G, Nicholls E, et al. . Subsets of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in community-dwelling older adults in the United kingdom: prevalence, inter-relationships, risk factor profiles and clinical characteristics at baseline and 3-years. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013;21:1674–84. 10.1016/j.joca.2013.08.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Spacek E, Poiraudeau S, Fayad F, et al. . Disability induced by hand osteoarthritis: are patients with more symptoms at digits 2-5 Interphalangeal joints different from those with more symptoms at the base of the thumb? osteoarthritis and cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2004;12:366–73. 10.1016/j.joca.2004.01.005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
