Resistin serum levels and its association with clinical profile and carotid intima-media thickness in psoriasis: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37355349
- PMCID: PMC10589471
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abd.2022.10.011
Resistin serum levels and its association with clinical profile and carotid intima-media thickness in psoriasis: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis is a protean disease associated with several comorbidities that may have increased levels of adiponectin such as resistin. This may affect the patients atherosclerotic risk.
Objective: To study resistin levels in a sample of Brazilian patients with psoriasis and its association with clinical profile, comorbidities, and carotid Intima-Media Thickness (cIMT).
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study of 119 individuals: 34 healthy controls and 85 patients with psoriasis, 42 of which with skin involvement only and 43 with psoriatic arthritis. Clinical and epidemiological data, measurement of PASI (Psoriasis Area Severity Index) and DAPSA (Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis), lipid profile, cIMT by ultrasound were collected from medical records. Resistin serum levels were measured by ELISA.
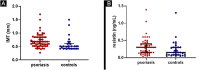
Results: Patients with psoriasis had higher resistin levels (p=0.009) and worse cIMT (p=0.0002) than controls. In the psoriasis sample, no associations of resistin levels with epidemiological, clinical findings, and activity indexes were found. Resistin serum levels were associated with the presence of diabetes (p=0.008) and metabolic syndrome (p=0.01) and correlated with total cholesterol (r=0.26) and triglycerides (r=0.33) but not with cIMT.
Study limitations: This work is limited by its transversal design and by the limited number of patients included.
Conclusion: Resistin serum levels are elevated in psoriasis patients. In this sample, clinical, epidemiological, and activity indexes were not linked to resistin serum levels, but atherosclerotic risk factors were.
Keywords: Arthritis; Atherosclerosis; Psoriasis; Psoriatic; Resistin.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U.
Figures
References
-
- Steppan C.M., Lazar M.A. Resistin and obesity-associated insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002;13:18–23. - PubMed
-
- Li F., He J., Li Z., Luo Z., Yan L., Li Y. Effects of resistin expression on glucose metabolism and hepatic insulin resistance. Endocrine. 2009;35:243–251. - PubMed
-
- Palanivel R., Maida A., Liu Y., Sweeney G. Regulation of insulin signalling, glucose uptake and metabolism in rat skeletal muscle cells upon prolonged exposure to resistin. Diabetologia. 2006;49:183–190. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

