Development and external validation of a novel nomogram to predict intravesical recurrence after radical nephroureterectomy: a multicenter study
- PMID: 37355502
- PMCID: PMC11796536
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05016-2
Development and external validation of a novel nomogram to predict intravesical recurrence after radical nephroureterectomy: a multicenter study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to establish and validate nomograms to predict the probability of intravesical recurrence (IVR) after radical nephroureterectomy (RNU) for upper urinary tract epithelial carcinoma (UTUC).
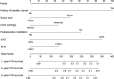
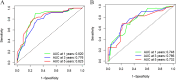
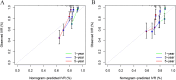
Methods: Clinical data of 528 patients with UTUC after RNU were collected from two medical centers between 2009 and 2020. We used the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression to select variables for multivariable Cox regression analysis in the training cohort and included independent risk factors into nomogram models predicting IVR-free survival (IVRFS). Another center was applied as the external cohort to validate the predictive accuracy and discriminative ability of the nomogram by performing area under the receiver operating curve (AUC), consistency index (C-index), and calibration curve.
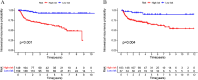
Results: History of bladder cancer, tumor size, preoperative urine cytology, postoperative instillation, Ki-67, and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were identified as independent risk factors for IVR. The prognosis model including these predictors demonstrated excellent discriminatory performance in both the training cohort (C-index, 0.814) and external validation cohort (C-index, 0.748). The calibration plots of the nomogram revealed good consistency in both cohorts. Finally, patients could be classified into two risk groups based on scores obtained from the nomogram, with significant differences in IVRFS.
Conclusion: Our study provided a reliable nomogram for predicting the probability of IVR in patients with UTUC after RNU. Risk stratification based on this model may assist urologists make optimal clinical decisions on the management of UTUC.
Keywords: Intravesical recurrence; Nomogram; Radical nephroureterectomy; Upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this study has received no financial support and there was no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel nomogram for predicting extraurothelial recurrence in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(15):14241-14253. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05237-5. Epub 2023 Aug 9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37555950 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram based on geriatric nutritional risk index for predicting prognosis and postoperative complications in surgical patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(20):18185-18200. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05462-y. Epub 2023 Nov 30. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38032382 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a novel immune and nutritional score on prognosis in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma following radical nephroureterectomy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(12):10893-10909. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04977-8. Epub 2023 Jun 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37318591 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinicopathologic Factors Linked to Intravesical Recurrence After Radical Nephroureterectomy to Treat Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2015 Jun;67(6):1122-1133. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.11.035. Epub 2014 Dec 6. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25488681
-
Oncologic Outcomes of Kidney-sparing Surgery Versus Radical Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: A Systematic Review by the EAU Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Guidelines Panel.Eur Urol. 2016 Dec;70(6):1052-1068. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.07.014. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 27477528
Cited by
-
Predictive Value of the Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio for Intravesical Recurrence After Radical Nephroureterectomy: A Retrospective Study.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Dec 11;17:10819-10833. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S483242. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39677281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agha R, Abdall-Razak A, Crossley E, Dowlut N, Iosifidis C, Mathew G et al (2019) STROCSS 2019 Guideline: strengthening the reporting of cohort studies in surgery. Int J Surg 72:156–165 - PubMed
-
- Azémar MD, Comperat E, Richard F, Cussenot O, Rouprêt M (2011) Bladder recurrence after surgery for upper urinary tract urothelial cell carcinoma: frequency, risk factors, and surveillance. Urol Oncol 29(2):130–136 - PubMed
-
- Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL (2004) X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res 10(21):7252–7259 - PubMed
-
- Chen CH, Dickman KG, Huang CY, Moriya M, Shun CT, Tai HC et al (2013) Aristolochic acid-induced upper tract urothelial carcinoma in Taiwan: clinical characteristics and outcomes. Int J Cancer 133(1):14–20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

