The risks of the new morbidities acquired during pediatric onco-critical care and their life-shortening effects
- PMID: 37356812
- PMCID: PMC10594009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jped.2023.05.006
The risks of the new morbidities acquired during pediatric onco-critical care and their life-shortening effects
Abstract
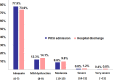
Objective: The authors investigated the functional status at ICU admission and at hospital discharge, and the impact of dysfunctions on survivors' lifespan.
Method: Single-center retrospective cohort. The FSS (Functional Status Scale) was calculated at ICU admission and at hospital discharge. A new morbidity was defined as an increase in FSS ≥ 3.
Results: Among 1002 patients, there were 855 survivors. Of these, 194 (22.6%) had died by the end of the study; 45 (5.3%) had a new morbidity. Means in the motor domain at admission and discharge were 1.37 (SD: 0.82) and 1.53 (SD 0.95, p = 0.002). In the feeding domain, the means were 1.19 (SD 0.63) and 1.30 (SD 0.76), p = 0.002; global means were 6.93 (SD 2.45) and 7.2 (SD 2.94), p = 0.007. Acute respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, the score PRISM IV, age < 5 years, and central nervous system tumors were independent predictors of new morbidity. New morbidity correlated with lower odds of survival after hospital discharge, considering all causes of death (p = 0.014), and was independently predictive of death (Cox hazard ratio = 1.98). In Weibull models, shortening in the life span of 14.2% (p = 0.014) was estimated as a new morbidity.
Conclusions: New morbidities are related to age, disease severity at admission, and SNC tumors. New morbidities, in turn, correlate with lower probabilities of survival and shortening of the remaining life span. Physical rehabilitation interventions in this population of children may have the potential to provide an increase in lifespan.
Keywords: Cancer survivor, childhood; Critical care outcomes; Expectancy, healthy life; Functional status.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Out of the PICU and Beyond!J Pediatr (Rio J). 2023 Nov-Dec;99(6):531-533. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2023.08.001. Epub 2023 Aug 26. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2023. PMID: 37643719 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pollack M.M., Holubkov R., Funai T., Clark A., Berger J.T., Meert K., et al. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Collaborative Pediatric Critical Care Research Network: pediatric intensive care outcomes: development of new morbidities during pediatric critical care. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014;15:821–827. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dalton H.J., Slonim A.D., Pollack M.M. MultiCenter outcome of pediatric oncology patients requiring intensive care. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2003;20:643–649. - PubMed
-
- Wösten-van Asperen R.M., van Gestel J.P., van Grotel M., Tschiedel E., Dohna-Schwake C., Valla F.V., et al. PICU mortality of children with cancer admitted to pediatric intensive care unit a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019;142:153–163. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

