Regorafenib prevents the development of emphysema in a murine elastase model
- PMID: 37357536
- PMCID: PMC10471461
- DOI: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0072
Regorafenib prevents the development of emphysema in a murine elastase model
Abstract
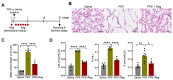
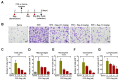
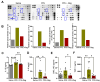
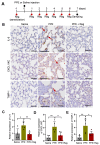
Emphysema is a chronic obstructive lung disease characterized by inflammation and enlargement of the air spaces. Regorafenib, a potential senomorphic drug, exhibited a therapeutic effect in porcine pancreatic elastase (PPE)-induced emphysema in mice. In the current study we examined the preventive role of regorafenib in development of emphysema. Lung function tests and morphometry showed that oral administration of regorafenib (5 mg/kg/day) for seven days after instillation of PPE resulted in attenuation of emphysema. Mechanistically, regorafenib reduced the recruitment of inflammatory cells, particularly macrophages and neutrophils, in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. In agreement with these findings, measurements using a cytokine array and ELISA showed that expression of inflammatory mediators including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and CXCL1/KC, and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloprotease-1 (TIMP-1), was downregulated. The results of immunohistochemical analysis confirmed that expression of IL-6, CXCL1/KC, and TIMP-1 was reduced in the lung parenchyma. Collectively, the results support the preventive role of regorafenib in development of emphysema in mice and provide mechanistic insights into prevention strategies. [BMB Reports 2023; 56(8): 439-444].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of neuropeptide Y against elastase-induced pulmonary emphysema.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022 Apr 1;322(4):L539-L549. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00353.2020. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35107033
-
IL-23 Is Essential for the Development of Elastase-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Emphysema.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Nov;55(5):697-707. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0015OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27351934
-
Loss of IL-33 enhances elastase-induced and cigarette smoke extract-induced emphysema in mice.Respir Res. 2021 May 15;22(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01705-z. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 33992109 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor Agonist Protects Mice Against Pulmonary Emphysema Induced by Elastase.Inflammation. 2024 Jun;47(3):958-974. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01953-9. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38227123
-
Inflammatory Cellular Response to Mechanical Ventilation in Elastase-Induced Experimental Emphysema: Role of Preexisting Alveolar Macrophages Infiltration.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Dec 19;2018:5721293. doi: 10.1155/2018/5721293. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30662910 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regorafenib as a potential drug for severe COVID-19: inhibition of inflammasome activation in mice.FEBS Open Bio. 2025 Mar;15(3):427-435. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.70002. Epub 2025 Feb 3. FEBS Open Bio. 2025. PMID: 39895416 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting accelerated pulmonary ageing to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-induced neuropathological comorbidities.Br J Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;181(1):3-20. doi: 10.1111/bph.16263. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37828646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regorafenib Attenuates Osteoclasts Differentiation by Inhibiting the NF-κB, NFAT, ERK, and p38 Signaling Pathways.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 23;9(31):33574-33593. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01308. eCollection 2024 Aug 6. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39130575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abboud RT, Vimalanathan S. Pathogenesis of COPD. Part I. The role of protease-antiprotease imbalance in emphysema. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008;12:361–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

