Hsa_circ_0005085 may suppress cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis through targeting the miR-186-5p/LAMC1 axis
- PMID: 37357644
- PMCID: PMC10262883
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13321
Hsa_circ_0005085 may suppress cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis through targeting the miR-186-5p/LAMC1 axis
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION: Hsa_circ_0005085 May Suppress Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth and Metastasis Through Targeting the MiR-186-5p/LAMC1 Axis.Skin Res Technol. 2025 Feb-May;31(2-5):e70181. doi: 10.1111/srt.70181. Skin Res Technol. 2025. PMID: 40371727 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
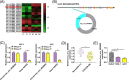
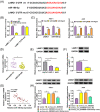
Background: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) is a severe malignancy derived from the skin. Mounting evidence suggests that circular RNAs (circRNAs) participate in diverse biological functions in human cancers, containing CSCC. However, the biological functions and underlying mechanism of hsa_circ_0005085 in CSCC have not been clearly studied.
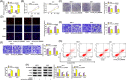
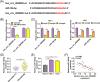
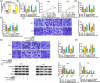
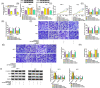
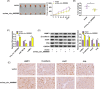
Methods: Expression levels of hsa_circ_0005085, microRNA-186-5p (miR-186-5p), and Laminin subunit gamma 1 (LAMC1) were detected by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Cell counting kit-8 assay, colony formation assay, and 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine assay were used to assess cell proliferation. Transwell assay was conducted to detect cell migration and invasion. Cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry. Protein expression of LAMC1, E-cadherin, Snail, and slug were assessed using western blot assay. Using bioinformatics software, the binding between miR-186-5p and hsa_circ_0005085 or LAMC1 was predicted, followed by verification using a dual-luciferase reporter and RNA-Immunoprecipitation. The mouse xenograft model was established to investigate the role of hsa_circ_0005085 in vivo.
Results: Hsa_circ_0005085 level was downregulated in CSCC tissues and cells. Overexpression of hsa_circ_0005085 inhibited cell proliferation, migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and promoted cell apoptosis in CSCC. MiR-186-5p could restore the effect of hsa_circ_0005085 overexpression on CSCC cells, and the knockdown of LAMC1 reversed the regulation of the miR-186-5p inhibitor. In mechanism, hsa_circ_0005085 served as a sponge for miR-186-5p to regulate LAMC1 expression. Overexpression of hsa_circ_0005085 reduced growth of tumor via miR-186-5p/LAMC1 axis in vivo.
Conclusion: In our study, hsa_circ_0005085 might inhibit CSCC development by targeting the miR-186-5p/LAMC1 axis, which might provide a promising therapeutic target for CSCC.
Keywords: Hsa_circ_0005085; LAMC1; cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; miR-186-5p.
© 2023 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cheng J, Yan S. Prognostic variables in high‐risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a review. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43(11):994‐1004. - PubMed
-
- Lomas A, Leonardi‐Be J, Bath‐Hextall FA. A systemic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1069‐1080. - PubMed
-
- Waldman A, Schmults C. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33(1):1‐12. - PubMed
-
- Que SKT, Zwald FO, Schmults CD. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: incidence, risk factors, diagnosis, and staging. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(2):237‐247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

