Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel benzoylhydrazone derivatives as Nur77 modulators with potent antitumor activity against hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37357764
- PMCID: PMC10294756
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2227777
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel benzoylhydrazone derivatives as Nur77 modulators with potent antitumor activity against hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
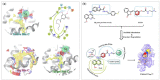
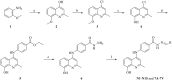
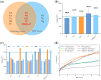
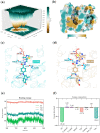
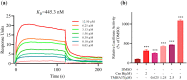
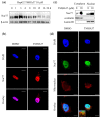
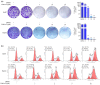
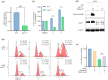
Nur77 modulators have emerged as a promising therapeutic approach for hepatocellular carcinoma. In this study, a structure-based rational drug design approach was used to design and synthesise a series of 4-((8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-4-yl)amino)benzoylhydrazone derivatives based on the binding characteristics of our previously reported 10g and the native ligand 3NB at the binding Site C of Nur77. Cell-based cytotoxicity assays revealed that compound TMHA37 demonstrated the highest cytotoxicity against all tested cancer cells. The induced fit docking and binding pose metadynamics simulation suggested that TMHA37 was the most promising Nur77 binder at Site C. Molecular dynamics simulation validated the stable binding of TMHA37 to Nur77's Site C but not to Sites A or B. Specifically, TMHA37 bound strongly to Nur77-LBD (KD = 445.3 nM) and could activate Nur77's transcriptional activity. Furthermore, TMHA37 exhibited antitumor effects by blocking the cell cycle at G2/M phase and inducing cell apoptosis in a Nur77-dependent manner.
Keywords: Benzoylhydrazone derivatives; Nur77; antitumor activity; hepatocellular carcinoma; molecular dynamics simulation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 5-((8-methoxy-2-methylquinolin-4-yl)amino)-1H-indole-2-carbohydrazide derivatives as novel Nur77 modulators.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 15;204:112608. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112608. Epub 2020 Jul 19. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32717483
-
Synthesis, SAR study, and bioactivity evaluation of a series of Quinoline-Indole-Schiff base derivatives: Compound 10E as a new Nur77 exporter and autophagic death inducer.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Aug;113:105008. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105008. Epub 2021 May 23. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34089944
-
Discovery of 5-((4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide derivatives as novel anti-cancer agents targeting Nur77.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Dec 15;244:114849. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114849. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36274272
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of N1-(2-(adamantan-1-yl)-1H-indol-5-yl)-N2-(substituent)-1,2-dicarboxamides as anticancer agents targeting Nur77-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress.Bioorg Chem. 2025 Feb;155:108113. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.108113. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Bioorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 39787915
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of a novel exceptionally potent and orally active Nur77 ligand NB1 with a distinct binding mode for cancer therapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Dec;14(12):5493-5504. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.07.012. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39807329 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
