Decellularization-Based Quantification of Skeletal Muscle Fatty Infiltration
- PMID: 37358301
- PMCID: PMC10837739
- DOI: 10.3791/65461
Decellularization-Based Quantification of Skeletal Muscle Fatty Infiltration
Abstract
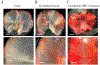
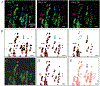
Fatty infiltration is the accumulation of adipocytes between myofibers in skeletal muscle and is a prominent feature of many myopathies, metabolic disorders, and dystrophies. Clinically in human populations, fatty infiltration is assessed using noninvasive methods, including computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound (US). Although some studies have used CT or MRI to quantify fatty infiltration in mouse muscle, costs and insufficient spatial resolution remain challenging. Other small animal methods utilize histology to visualize individual adipocytes; however, this methodology suffers from sampling bias in heterogeneous pathology. This protocol describes the methodology to qualitatively view and quantitatively measure fatty infiltration comprehensively throughout intact mouse muscle and at the level of individual adipocytes using decellularization. The protocol is not limited to specific muscles or specific species and can be extended to human biopsy. Additionally, gross qualitative and quantitative assessments can be made with standard laboratory equipment for little cost, making this procedure more accessible across research laboratories.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES:
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
