Highly Networked SARS-CoV-2 Peptides Elicit T Cell Responses with Enhanced Specificity
- PMID: 37358499
- PMCID: PMC10580120
- DOI: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2300034
Highly Networked SARS-CoV-2 Peptides Elicit T Cell Responses with Enhanced Specificity
Abstract
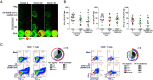
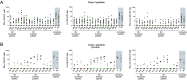
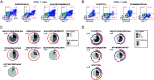
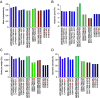
Identifying SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell epitope-derived peptides is critical for the development of effective vaccines and measuring the duration of specific SARS-CoV-2 cellular immunity. In this regard, we previously identified T cell epitope-derived peptides within topologically and structurally essential regions of SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins by applying an immunoinformatics pipeline. In this study, we selected 30 spike- and nucleocapsid-derived peptides and assessed whether these peptides induce T cell responses and avoid major mutations found in SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Our peptide pool was highly specific, with only a single peptide driving cross-reactivity in people unexposed to SARS-COV-2, and immunogenic, inducing a polyfunctional response in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from COVID-19 recovered individuals. All peptides were immunogenic and individuals recognized broad and diverse peptide repertoires. Moreover, our peptides avoided most mutations/deletions associated with all four SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern while retaining their physicochemical properties even when genetic changes are introduced. This study contributes to an evolving definition of individual CD4+ and CD8+ T cell epitopes that can be used for specific diagnostic tools for SARS-CoV-2 T cell responses and is relevant to the development of variant-resistant and durable T cell-stimulating vaccines.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Spike T-Cell Epitopes for Assessing T-Cell Immunity.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02002-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02002-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33443088 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 specific memory T cell epitopes identified in COVID-19-recovered subjects.Virus Res. 2021 Oct 15;304:198508. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198508. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Virus Res. 2021. PMID: 34329696 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of a synthetic peptide vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 inducing multiepitopic and cross-reactive humoral neutralizing and cellular CD4 and CD8 responses.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):1931-1946. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1978823. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 34538222 Free PMC article.
-
Degenerate CD8 Epitopes Mapping to Structurally Constrained Regions of the Spike Protein: A T Cell-Based Way-Out From the SARS-CoV-2 Variants Storm.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 8;12:730051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.730051. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34566990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of multi-epitope peptide-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2.Biomed J. 2021 Mar;44(1):18-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 33727051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
T Cell Peptide Prediction, Immune Response, and Host-Pathogen Relationship in Vaccinated and Recovered from Mild COVID-19 Subjects.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 26;14(10):1217. doi: 10.3390/biom14101217. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456150 Free PMC article.
-
Bivalent Omicron BA.1 vaccine booster increases memory B cell breadth and neutralising antibodies against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.EBioMedicine. 2024 Dec;110:105461. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105461. Epub 2024 Nov 28. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39612651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galani, I. E., Rovina N., Lampropoulou V., Triantafyllia V., Manioudaki M., Pavlos E., Koukaki E., Fragkou P. C., Panou V., Rapti V., et al. . 2021. Untuned antiviral immunity in COVID-19 revealed by temporal type I/III interferon patterns and flu comparison. Nat. Immunol. 22: 32–40. - PubMed
-
- Tan, A. T., Linster M., Tan C. W., Le Bert N., Chia W. N., Kunasegaran K., Zhuang Y., Tham C. Y. L., Chia A., Smith G. J. D., et al. . 2021. Early induction of functional SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells associates with rapid viral clearance and mild disease in COVID-19 patients. Cell Rep. 34: 108728. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

