Energetic Stress-Induced Metabolic Regulation by Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 37358503
- PMCID: PMC10414774
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c230001
Energetic Stress-Induced Metabolic Regulation by Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
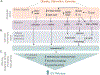
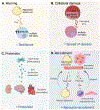
Recent studies have demonstrated that extracellular vesicles (EVs) serve powerful and complex functions in metabolic regulation and metabolic-associated disease, although this field of research is still in its infancy. EVs are released into the extracellular space from all cells and carry a wide range of cargo including miRNAs, mRNA, DNA, proteins, and metabolites that have robust signaling effects in receiving cells. EV production is stimulated by all major stress pathways and, as such, has a role in both restoring homeostasis during stress and perpetuating disease. In metabolic regulation, the dominant stress signal is a lack of energy due to either nutrient deficits or damaged mitochondria from nutrient excess. This stress signal is termed "energetic stress," which triggers a robust and evolutionarily conserved response that engages major cellular stress pathways, the ER unfolded protein response, the hypoxia response, the antioxidant response, and autophagy. This article proposes the model that energetic stress is the dominant stimulator of EV release with a focus on metabolically important cells such as hepatocytes, adipocytes, myocytes, and pancreatic β-cells. Furthermore, this article will discuss how the cargo in stress-stimulated EVs regulates metabolism in receiving cells in both beneficial and detrimental ways. © 2023 American Physiological Society. Compr Physiol 13:5051-5068, 2023.
Copyright © 2023 American Physiological Society. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles in metabolic disease.Diabetologia. 2019 Dec;62(12):2179-2187. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05014-5. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 31690986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolism and Metabolic Diseases.Subcell Biochem. 2021;97:393-410. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-67171-6_15. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33779925
-
Post-translational protein deimination signatures in sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) plasma and plasma-extracellular vesicles.Dev Comp Immunol. 2021 Dec;125:104225. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2021.104225. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Dev Comp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34358577
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Endocannabinoid Signaling in Patients with COVID-19.Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2024 Oct;9(5):1326-1338. doi: 10.1089/can.2023.0040. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2024. PMID: 37713293
-
The effect of extracellular vesicles on the regulation of mitochondria under hypoxia.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Apr 6;12(4):358. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03640-9. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33824273 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Other Liver Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 23;26(11):5033. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115033. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise mediates myocardial infarction via non-coding RNAs.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Nov 1;11:1432468. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1432468. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39553846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping Organism-wide Single Cell mRNA Expression Linked to Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis, Secretion, and Cargo.Function (Oxf). 2025 Mar 24;6(2):zqaf005. doi: 10.1093/function/zqaf005. Function (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 39863422 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: Advanced Tools for Disease Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 29;26(1):189. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010189. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain penetration of peripheral extracellular vesicles from Alzheimer's patients and induction of microglia activation.J Extracell Biol. 2025 Jan 17;4(1):e70027. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70027. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Extracell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39830834 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

