Extracellular Vesicles in Hepatobiliary Health and Disease
- PMID: 37358519
- PMCID: PMC10798368
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c210046
Extracellular Vesicles in Hepatobiliary Health and Disease
Abstract
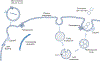
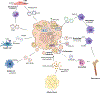
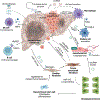
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-bound nanoparticles released by cells and are an important means of intercellular communication in physiological and pathological states. We provide an overview of recent advances in the understanding of EV biogenesis, cargo selection, recipient cell effects, and key considerations in isolation and characterization techniques. Studies on the physiological role of EVs have relied on cell-based model systems due to technical limitations of studying endogenous nanoparticles in vivo . Several recent studies have elucidated the mechanistic role of EVs in liver diseases, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, viral hepatitis, cholestatic liver disease, alcohol-associated liver disease, acute liver injury, and liver cancers. Employing disease models and human samples, the biogenesis of lipotoxic EVs downstream of endoplasmic reticulum stress and microvesicles via intracellular activation stress signaling are discussed in detail. The diverse cargoes of EVs including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids can be enriched in a disease-specific manner. By carrying diverse cargo, EVs can directly confer pathogenic potential, for example, recruitment and activation of monocyte-derived macrophages in NASH and tumorigenicity and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. We discuss the pathogenic role of EVs cargoes and the signaling pathways activated by EVs in recipient cells. We review the literature that EVs can serve as biomarkers in hepatobiliary diseases. Further, we describe novel approaches to engineer EVs to deliver regulatory signals to specific cell types, and thus use them as therapeutic shuttles in liver diseases. Lastly, we identify key lacunae and future directions in this promising field of discovery and development. © 2023 American Physiological Society. Compr Physiol 13:4631-4658, 2023.
Copyright © 2023 American Physiological Society. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles in NAFLD/ALD: From Pathobiology to Therapy.Cells. 2020 Mar 27;9(4):817. doi: 10.3390/cells9040817. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32231001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging roles of extracellular vesicles as intercellular messengers in liver physiology and pathology.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2022 Oct;28(4):706-724. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0390. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35232008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in liver pathobiology: Small particles with big impact.Hepatology. 2016 Dec;64(6):2219-2233. doi: 10.1002/hep.28814. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 27628960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of extracellular vesicles in liver diseases.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):G739-G749. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00183.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31545919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The promise of small particles: extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in liver pathology.J Physiol. 2023 Nov;601(22):4953-4971. doi: 10.1113/JP283074. Epub 2022 Jul 1. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 35708653 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunology and treatments of fatty liver disease.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jan;99(1):127-152. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03920-1. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39692857 Review.
-
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Other Liver Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 23;26(11):5033. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115033. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Liver Diseases.Viruses. 2024 Nov 17;16(11):1785. doi: 10.3390/v16111785. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39599900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycolysis in hepatic stellate cells coordinates fibrogenic extracellular vesicle release spatially to amplify liver fibrosis.Sci Adv. 2024 Jun 28;10(26):eadn5228. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn5228. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38941469 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Micro-RNAs in Liver Disease.Semin Liver Dis. 2025 Jun;45(2):167-179. doi: 10.1055/a-2494-2233. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Semin Liver Dis. 2025. PMID: 39626790 Review.
References
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C, Lakhal S, Wood MJ. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol 29: 341–345, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Anger F, Camara M, Ellinger E, Germer CT, Schlegel N, Otto C, Klein I. Human mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles improve liver regeneration after ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. Stem Cells Dev 28: 1451–1462, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Angioni R, Cali B, Vigneswara V, Crescenzi M, Merino A, Sanchez-Rodriguez R, Liboni C, Hoogduijn MJ, Newsome PN, Muraca M, Russo FP, Viola A. Administration of human MSC-derived extracellular vesicles for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: Preclinical data in MDR2 knockout mice. Int J Mol Sci 21: 8874, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

