Efficacy and Safety of Butylphthalide in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37358859
- PMCID: PMC10294018
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.1871
Efficacy and Safety of Butylphthalide in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: DL-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) is a drug for treating acute ischemic stroke and may play a neuroprotective role by acting on multiple active targets. The efficacy of NBP in patients with acute ischemic stroke receiving reperfusion therapy remains unknown.
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of NBP in patients with acute ischemic stroke receiving reperfusion therapy of intravenous thrombolysis and/or endovascular treatment.
Design, setting, and participants: This multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel randomized clinical trial was conducted in 59 centers in China with 90-day follow-up. Of 1236 patients with acute ischemic stroke, 1216 patients 18 years and older diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke with a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score ranging from 4 to 25 who could start the trial drug within 6 hours from symptom onset and received either intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) or endovascular treatment or intravenous rt-PA bridging to endovascular treatment were enrolled, after excluding 20 patients who declined to participate or did not meet eligibility criteria. Data were collected from July 1, 2018, to May 22, 2022.
Interventions: Within 6 hours after symptom onset, patients were randomized to receive NBP or placebo in a 1:1 ratio.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary efficacy outcome was the proportion of patients with a favorable outcome based on 90-day modified Rankin Scale score (a global stroke disability scale ranging from 0 [no symptoms or completely recovered] to 6 [death]) thresholds of 0 to 2 points, depending on baseline stroke severity.
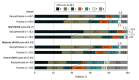
Results: Of 1216 enrolled patients, 827 (68.0%) were men, and the median (IQR) age was 66 (56-72) years. A total of 607 were randomly assigned to the butylphthalide group and 609 to the placebo group. A favorable functional outcome at 90 days occurred in 344 patients (56.7%) in the butylphthalide group and 268 patients (44.0%) in the placebo group (odds ratio, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.35-2.14; P < .001). Serious adverse events within 90 days occurred in 61 patients (10.1%) in the butylphthalide group and 73 patients (12.0%) in the placebo group.
Conclusions and relevance: Among patients with acute ischemic stroke receiving intravenous thrombolysis and/or endovascular treatment, NBP was associated with a higher proportion of patients achieving a favorable functional outcome at 90 days compared with placebo.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03539445.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Hacke W, Donnan G, Fieschi C, et al. ; ATLANTIS Trials Investigators; ECASS Trials Investigators; NINDS rt-PA Study Group Investigators . Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt-PA stroke trials. Lancet. 2004;363(9411):768-774. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15692-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. ; American Heart Association Stroke Council . 2018 Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49(3):e46-e110. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000158 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. . Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344-e418. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000211 - DOI - PubMed

