Immunization with a mucosal, post-fusion F/G protein-based polyanhydride nanovaccine protects neonatal calves against BRSV infection
- PMID: 37359514
- PMCID: PMC10289034
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186184
Immunization with a mucosal, post-fusion F/G protein-based polyanhydride nanovaccine protects neonatal calves against BRSV infection
Abstract
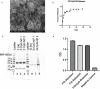
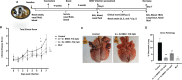
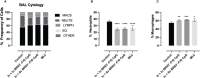
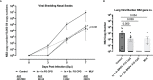
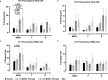
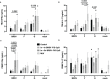
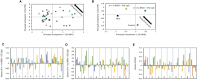
Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is a leading cause of death in young children and there are no FDA approved vaccines. Bovine RSV (BRSV) is antigenically similar to HRSV, and the neonatal calf model is useful for evaluation of HRSV vaccines. Here, we determined the efficacy of a polyanhydride-based nanovaccine encapsulating the BRSV post-fusion F and G glycoproteins and CpG, delivered prime-boost via heterologous (intranasal/subcutaneous) or homologous (intranasal/intranasal) immunization in the calf model. We compared the performance of the nanovaccine regimens to a modified-live BRSV vaccine, and to non-vaccinated calves. Calves receiving nanovaccine via either prime-boost regimen exhibited clinical and virological protection compared to non-vaccinated calves. The heterologous nanovaccine regimen induced both virus-specific cellular immunity and mucosal IgA, and induced similar clinical, virological and pathological protection as the commercial modified-live vaccine. Principal component analysis identified BRSV-specific humoral and cellular responses as important correlates of protection. The BRSV-F/G CpG nanovaccine is a promising candidate vaccine to reduce RSV disease burden in humans and animals.
Keywords: bovine respiratory disease; bovine respiratory syncytial virus; human respiratory syncytial virus; immunology; nanoparticles; nanovaccines; neonatal calf model.
Copyright © 2023 Maina, Grego, Broderick, Sacco, Narasimhan and McGill.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shi T, McAllister DA, O'Brien KL, Simoes EAF, Madhi SA, Gessner GD. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: a systematic review and modelling study. Lancet (2017) 390:946–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30938-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

