Recent Developments in Equilibrium Optimizer Algorithm: Its Variants and Applications
- PMID: 37359743
- PMCID: PMC10096115
- DOI: 10.1007/s11831-023-09923-y
Recent Developments in Equilibrium Optimizer Algorithm: Its Variants and Applications
Abstract
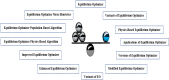
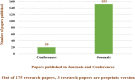
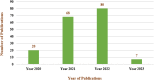
There have been many algorithms created and introduced in the literature inspired by various events observable in nature, such as evolutionary phenomena, the actions of social creatures or agents, broad principles based on physical processes, the nature of chemical reactions, human behavior, superiority, and intelligence, intelligent behavior of plants, numerical techniques and mathematics programming procedure and its orientation. Nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithms have dominated the scientific literature and have become a widely used computing paradigm over the past two decades. Equilibrium Optimizer, popularly known as EO, is a population-based, nature-inspired meta-heuristics that belongs to the class of Physics based optimization algorithms, enthused by dynamic source and sink models with a physics foundation that are used to make educated guesses about equilibrium states. EO has achieved massive recognition, and there are quite a few changes made to existing EOs. This article gives a thorough review of EO and its variations. We started with 175 research articles published by several major publishers. Additionally, we discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the algorithms to help researchers find the variant that best suits their needs. The core optimization problems from numerous application areas using EO are also covered in the study, including image classification, scheduling problems, and many others. Lastly, this work recommends a few potential areas for EO research in the future.
© The Author(s) under exclusive licence to International Center for Numerical Methods in Engineering (CIMNE) 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fausto F, Reyna-Orta A, Cuevas E, Andrade ÁG, Perez-Cisneros M. From ants to whales: metaheuristics for all tastes. Artif Intell Rev. 2020;53(1):753–810. doi: 10.1007/s10462-018-09676-2. - DOI
-
- Dorigo M Di Caro G (1999) Ant colony optimization: a new meta-heuristic. In: Proceedings of the 1999 congress on evolutionary computation-CEC99 (Cat. No. 99TH8406). IEEE vol 2 pp 1470–1477
-
- Yang XS, Deb S (2010) Engineering optimisation by cuckoo search. arXiv preprint arXiv:1005.2908
-
- Karaboga D. Artificial bee colony algorithm. Scholarpedia. 2010;5(3):6915. doi: 10.4249/scholarpedia.6915. - DOI
-
- Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995, November) Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN'95-international conference on neural networks. IEEE. (Vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
