A nitrocellulose/cotton fiber hybrid composite membrane for paper-based biosensor
- PMID: 37360890
- PMCID: PMC10238769
- DOI: 10.1007/s10570-023-05288-4
A nitrocellulose/cotton fiber hybrid composite membrane for paper-based biosensor
Abstract
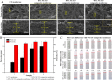
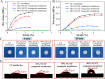
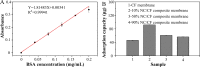
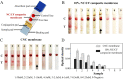
Nitrocellulose (NC) membrane was fabricated and tested for its potential use in various paper-based biosensors for use in point-of-care testing. However, contemporary technologies are complex, expensive, non-scalable, limited by conditions, and beset with potentially adverse effects on the environment. Herein, we proposed a simple, cost-effective, scalable technology to prepare nitrocellulose/cotton fiber (NC/CF) composite membranes. The NC/CF composite membranes with a diameter of 20 cm were fabricated in 15 min using papermaking technology, which contributes to scalability in the large-scale production of these composites. Compared with existing commercial NC membranes, the NC/CF composite membrane is characterized by small pore size (3.59 ± 0.19 μm), low flow rate (156 ± 55 s/40 mm), high dry strength (up to 4.04 MPa), and wet strength (up to 0.13 MPa), adjustable hydrophilic-hydrophobic (contact angles ranged from 29 ± 4.6 to 82.8 ± 2.4°), the good adsorption capacity of protein (up to 91.92 ± 0.07 μg). After lateral flow assays (LFAs) detection, the limit of detection is 1 nM, which is similar to commercial NC membrane (Sartorius CN 140). We envision the NC/CF composite membrane as a promising material for paper-based biosensors of point-of-care testing applications.
Keywords: Cotton fiber; Lateral flow assays; Nitrocellulose; Papermaking technology; Point-of-care testing.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmad AL, Low SC, Shukor SRA. Effects of membrane cast thickness on controlling the macrovoid structure in lateral flow nitrocellulose membrane and determination of its characteristics. Scripta Mater. 2007;57:743–746. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.06.037. - DOI
-
- Ahmad AL, Low SC, Shukor SRA, Ismail A. Synthesis and characterization of polymeric nitrocellulose membranes: Influence of additives and pore formers on the membrane morphology. J Appl Polym Sci. 2008;108:2550–2557. doi: 10.1002/app.27592. - DOI
-
- Cao S, Ge W, Yang Y, Huang Q, Wang X. High strength, flexible, and conductive graphene/polypropylene fiber paper fabricated via papermaking process. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma. 2021;5:104–112. doi: 10.1007/s42114-021-00374-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
