Oral manifestations associated with Novel Coronavirus Disease - 2019 (COVID-19): A questionnaire based hypothetical study
- PMID: 37360936
- PMCID: PMC10285348
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.128125.2
Oral manifestations associated with Novel Coronavirus Disease - 2019 (COVID-19): A questionnaire based hypothetical study
Abstract
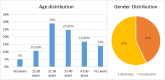
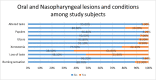
Background: Since the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in 2019, the virus has evolved drastically, presenting with sets of mutations that influence its properties, including transmissibility and antigenicity. The oral mucosa is postulated as probable portal entry and several oral manifestations have been identified, which places dental professionals in a position to recognize probable COVID-19 patients depending on oral signs and symptoms in the initial phases of the disease itself. As co-existing with COVID-19 seems to be a new reality, greater understanding is required regarding early oral signs and symptoms which can be predictors for timely intervention and prevention of complications in COVID-19 patients. The objective of the study is to identify the distinguishing oral signs and symptoms among COVID-19 patients and to establish possible correlation between severity of COVID-19 infection and oral symptoms. Methods: This study recruited 179 ambulatory, non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia's Eastern Province's designated hotels for COVID-19 and home isolated patients from the same region using a convenience sample method. Data was collected by qualified and experienced investigators, including two physicians and three dentists, using a validated comprehensive questionnaire through telephonic interviews with the participants. The X 2 was used to assess the categorical variables, and odd's ratio was calculated to determine the strength of the association between general symptoms and oral manifestations. Results: Oral and nasopharyngeal lesions or conditions like loss of smell and taste, xerostomia, sore throat, and burning sensation were predictors of COVID-19-related systemic symptoms such as cough, fatigue, fever, and nasal congestion were identified to be statistically significant (p<0.05). Conclusions: The study reveals the occurrence of olfactory or taste dysfunction, dry mouth, sore throat, and burning sensation along with COVID-19 generic symptoms, should be considered as suggestive yet not conclusive indicators of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; ageusia; anosmia; oral symptoms; prevalence; xerostomia..
Copyright: © 2023 MOHAMMED F et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Olfactory and Oral Manifestations of COVID-19: Sex-Related Symptoms-A Potential Pathway to Early Diagnosis.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Oct;163(4):722-728. doi: 10.1177/0194599820934380. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32539587 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Aug;277(8):2251-2261. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32253535 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 23;2(2):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5:CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. PMID: 33620086 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prevalence of taste and smell dysfunction in mild and asymptomatic COVID-19 patients during Omicron prevalent period in Shanghai, China: a cross-sectional survey study.BMJ Open. 2023 Mar 21;13(3):e067065. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067065. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 36944468 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Dysfunction in the COVID-19 Outbreak.J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2020;30(5):317-326. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0567. Epub 2020 May 14. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32406374 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Oral Lesions, Dysgeusia and Osteonecrosis Related to COVID-19: A Comprehensive Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 14;14(4):1267. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041267. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report-September 21, 2021. Edition 58.
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials