IRIDA-ARIES Genomics, a key player in the One Health surveillance of diseases caused by infectious agents in Italy
- PMID: 37361153
- PMCID: PMC10289303
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1151568
IRIDA-ARIES Genomics, a key player in the One Health surveillance of diseases caused by infectious agents in Italy
Erratum in
-
Erratum: IRIDA-ARIES Genomics, a key player in the One Health surveillance of diseases caused by infectious agents in Italy.Front Public Health. 2023 Sep 5;11:1276201. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1276201. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37736081 Free PMC article.
Abstract
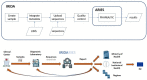
Pathogen genomics is transforming surveillance of infectious diseases, deepening our understanding of evolution and diffusion of etiological agents, host-pathogen interactions and antimicrobial resistance. This discipline is playing an important role in the development of One Health Surveillance with public health experts of various disciplines integrating methods applied to pathogen research, monitoring, management and prevention of outbreaks. Especially with the notion that foodborne diseases may not be transmitted by food only, the ARIES Genomics project aimed to deliver an Information System for the collection of genomic and epidemiological data to enable genomics-based surveillance of infectious epidemics, foodborne outbreaks and diseases at the animal-human interface. Keeping in mind that the users of the system comprised persons with expertise in a wide variety of domains, the system was expected to be used with a low learning curve directly by the persons target of the analyses' results, keeping the information exchange chains as short as possible. As a result, the IRIDA-ARIES platform (https://irida.iss.it/) provides an intuitive web-based interface for multisectoral data collection and bioinformatic analyses. In practice, the user creates a sample and uploads the Next-generation sequencing reads, then an analysis pipeline is launched automatically performing a series of typing and clustering operations fueling the information flow. Instances of IRIDA-ARIES host the Italian national surveillance system for infections by Listeria monocytogenes (Lm) and the surveillance system for infections by Shigatoxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC). As of today, the platform does not provide tools to manage epidemiological investigations but serves as an instrument of aggregation for risk monitoring, capable of triggering alarms on possible critical situations that might go unnoticed otherwise.
Keywords: One Health surveillance; data integration; foodborne pathogens; genomic; molecular typing workflows; multisectorial.
Copyright © 2023 Knijn, Michelacci, Gigliucci, Tozzoli, Chiani, Minelli, Scavia, Ventola and Morabito.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Food Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations World Organisation for Animal Health . Taking a Multisectoral, One Health Approach: A Tripartite Guide to Addressing Zoonotic Diseases in Countries. World Health Organization (2019). Available online at: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/325620 (accessed May 10, 2023).
-
- Dente MG, Riccardo F, Milano A, Robbiati C, Agrimi U, Morabito S, et al. . A One Health-based Conceptual Framework for comprehensive and coordinated prevention and preparedness to health threats. Int J Infect Dis. (2022) 116:S108–9. 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.12.256 - DOI
-
- Knijn A, Michelacci V, Orsini M, Morabito S. Advanced Research Infrastructure for Experimentation in genomicS (ARIES): a lustrum of Galaxy experience. bioRxiv preprint. (2020). 10.1101/2020.05.14.095901 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

