The application of multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified pencil graphite electrode for voltammetric determination of favipiravir used in COVID-19 treatment
- PMID: 37361695
- PMCID: PMC10249926
- DOI: 10.1007/s00706-023-03082-3
The application of multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified pencil graphite electrode for voltammetric determination of favipiravir used in COVID-19 treatment
Abstract
This study describes the first application of an improved procedure on a pencil graphite electrode decorated with functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (f-MWCNTs/PGE) for the determination of the COVID-19 antiviral drug, favipiravir (FVP). The electrochemical behavior of FVP at f-MWCNTs/PGE was examined by cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) methods, and it was noted that the voltammetric response significantly increased with the modification of f -MWCNTs to the surface. The linear range and limit of detection from DPV studies were determined as 1-1500 µM and 0.27 µM, respectively. In addition, the selectivity of the method was tested toward potential interferences, which can be present in pharmaceutical and biological samples, and it was found that f-MWCNTs/PGE showed high selectivity for the determination of FVP in the presence of probable interferences. The results with high accuracies and precisions from the obtained feasibility studies also revealed that the designed procedure can be used for accurate and selective voltammetric determination of FVP in real samples.
Keywords: Electrochemistry; Favipiravir; Functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes; Sensors voltammetry.
© Springer-Verlag GmbH Austria, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Figures
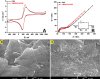


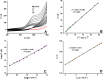

References
-
- Bouali W, Erk N, Kholafazadehastamal G, Naser M, Tiris G. Diam Relat Mater. 2023;131:109609. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109609. - DOI
-
- Kanbeş Dindar Ç, Bozal-Palabiyik B, Uslu B. Electroanalysis. 2022;34:1174. doi: 10.1002/elan.202100571. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard (2023) https://covid19.who.int/ Accessed: 2 Apr 2023
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
