Extra-Parotid Pleomorphic Adenoma and Low-Grade Salivary Malignancy in the Head and Neck Region
- PMID: 37362518
- PMCID: PMC10290231
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.39463
Extra-Parotid Pleomorphic Adenoma and Low-Grade Salivary Malignancy in the Head and Neck Region
Abstract
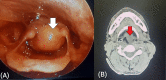
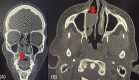
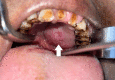
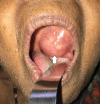
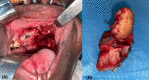
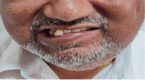
Background and objective Pleomorphic adenoma is the most common major salivary gland neoplasm. Around 80% of them arise in the parotid glands, whereas 10% originate in the minor salivary glands. The pleomorphic adenoma of the extra-parotid site is defined by its location outside the primary salivary gland. The minor salivary gland adenomas occur at the hard and soft palate, lips, tongue, lacrimal glands, pharynx, larynx, paranasal sinus, and nasal cavity. Pleomorphic adenoma in parapharyngeal space may occur de novo or as an extension of the deep lobe of the parotid tumors. Our objective in this study was to assess the location and presentations of extra-parotid pleomorphic adenoma and frequency of low-grade salivary gland malignancy diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma via fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the head and neck region and the treatment outcomes after the resection of the tumors. Materials and methods This was a retrospective observational study. All patients with FNAC-diagnosed pleomorphic adenoma of extra-parotid locations of the head and neck region who underwent curative surgery in the Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery at a rural tertiary care center between August 1997 and August 2022 were included in the study. Data on the symptoms, FNAC report, surgical techniques, pathological results, adjuvant therapy, and any recurrence were documented. Data were entered into a Microsoft Excel sheet and analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 22 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY). Results Our study included 23 patients, of which 14 were females and nine were males. The various sites of involvement were as follows: parapharyngeal space (four), larynx (one), nasal septum (two), hard palate (five), soft palate (four), hard and soft palate (three), and submandibular salivary gland (four). Of note, 17.3% of the patients had local recurrence with an average time frame of three years post-surgery: 20% in patients with low-grade malignancy and 16.6% in patients with pleomorphic adenoma. Conclusion Extra-parotid pleomorphic adenomas are common and have a high malignant potential. The preferred choice of treatment for extra-parotid salivary tumors is complete resection with adequate clearance. Malignant pleomorphic adenomas may require staging neck dissection and adjuvant treatment for a better prognosis.
Keywords: adenoid cystic carcinoma; extra-parotid salivary gland; mucoepidermoid; parapharyngeal space; pleomorphic adenoma; recurrence.
Copyright © 2023, Jose et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

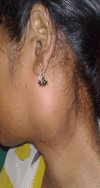


References
-
- Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum. Baron S, Koka V, El Chater P, Cucherousset J, Paoli C. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2014;131:139–141. - PubMed
-
- Surgical approaches to tumors of the parapharyngeal space. Stell PM, Mansfield AO, Stoney PJ. Am J Otolaryngol. 1985;6:92–97. - PubMed
-
- Giant deep lobe parotid gland pleomorphic adenoma involving the parapharyngeal space. Report of three cases and review of the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Sergi B, Limongelli A, Scarano E, Fetoni A, Paludetti G. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2689534/ Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2008;28:261–265. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
