Fog computing-assisted path planning for smart shopping
- PMID: 37362689
- PMCID: PMC10039442
- DOI: 10.1007/s11042-023-14926-9
Fog computing-assisted path planning for smart shopping
Abstract
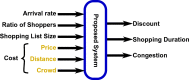
A Smart City (SC) is a viable solution for green and sustainable living, especially with the current explosion in global population and rural-urban immigration. One of the fields that is not getting much attention in the Smart Economy (SE) is customer satisfaction. The SE is a component of SC that is concerned with using Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to improve stages of the traditional economy. In this paper, we propose a fog computing-based shopping recommendation system. Our simulations used Al-Madinah city as a case study. It aims to improve the customer shopping experience. Customers in shopping malls can connect to the system via Wi-Fi. Then the system recommends products to the shoppers according to their preferences. It optimizes shoppers' schedules using price, the distance between the shops, and the congestion. It also improves customers' savings by up to 30%. It also increases the shopping speed by up to 6.12% compared to the system proposed in the literature.
Keywords: COVID-19; Internet of things; Pervasive computing; Smart cities; Smart shopping.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Aliyu F (2021) Fog computing-assisted path planning for smart shopping simulation code. https://github.com/faroouq/Smart-Shopping - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allam AK (2020) IKEA furniture: Kaggle. kaggle.com. Accessed on 15th May 2021. https://www.kaggle.com/ahmedkallam/ikea-sa-furniture-web-scraping/versio...
-
- Almalki FA, Alsamhi SH, Sahal R, Hassan J, Hawbani A, Rajput NS, Saif A, Morgan J, Breslin J (2021) Green iot for eco-friendly and sustainable smart cities: future directions and opportunities. Mobile Netw Appl. 10.1007/s11036-021-01790-w
-
- Anitta AD, Guddad SS, Anusha AS, Yanamala K, Sahithi SS (2021) Smart shopping cart using IOT and robotic arm:301–305. 10.1109/ICDI3C53598.2021.00067
-
- AnyLogic (2021) AnyLogic: simulation modeling software tools & solutions for business. Accessed on 16th November 2021. https://www.anylogic.com/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
