Anti-inflammatory potential of 1- O-methyl chrysophanol from Amycolatopsis thermoflava ICTA 103: an exploratory study
- PMID: 37363609
- PMCID: PMC10289675
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000466
Anti-inflammatory potential of 1- O-methyl chrysophanol from Amycolatopsis thermoflava ICTA 103: an exploratory study
Abstract
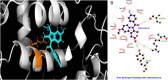
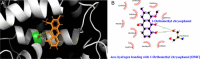
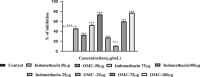
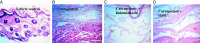
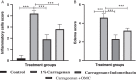
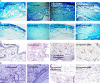
The present study was designed to investigate the anti-inflammatory potential of Amycolatopsis thermoflava producing 1-O-methyl chrysophanol (OMC), a member of the hydroxyanthraquinone family. The anti-inflammatory potential was evaluated initially through in silico analysis against tumor necrosis factor- α and cyclooxygenase-2. The same activity was further confirmed based on the in vitro protein denaturation method as well as in vivo by a carrageenan-induced paw edema model in rats. The OMC compound was isolated, purified, and characterized from the fermentation broth of Amycoloptosis thermoflava. In vitro data revealed that the OMC possesses significant protein denaturation properties with an IC50 of 63.50±2.19 µg/ml higher than the standard drug, with an IC50 value of 71.42±0.715 µg/ml. The percentage of inhibition in paw swelling was observed to be 40.03±5.5 in OMC-treated group, which is comparable to the standard group (52.8±4.7). The histopathological evaluation and immunohistochemistry revealed the anti-inflammatory potential of OMC.
Keywords: 1-O-methyl chrysophanol; amycolatopsis thermoflava; anti-inflammatory; carrageenan-induced paw edema model; molecular docking studies; protein denaturation.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


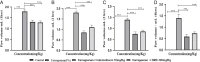
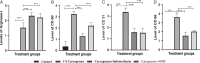
References
-
- Harikrishnan S, Jeemon P, Mini GK, et al. . GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2018;18:32203–32207. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tskhay A Yezhova A and Alibek K. COVID-19 Pandemic: Is Chronic Inflammation a Major Cause of Death? medRxiv . 2020. 10.1101/2020.05.12.20099572. - DOI
-
- Medzhitov R. Inflammation 2010: new adventures of an old flame. Cell 2010;140:771–776. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN, Savill J. Resolution of inflammation: the beginning programs the end. Nature immunology 2005;6:1191–1197. - PubMed
-
- Kumar V, Cotran RS, Robbins SL. Robbins Basic Pathology. Saunders; 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
