Deletion of Carboxypeptidase E in β-Cells Disrupts Proinsulin Processing but Does Not Lead to Spontaneous Development of Diabetes in Mice
- PMID: 37364047
- PMCID: PMC10450824
- DOI: 10.2337/db22-0945
Deletion of Carboxypeptidase E in β-Cells Disrupts Proinsulin Processing but Does Not Lead to Spontaneous Development of Diabetes in Mice
Abstract
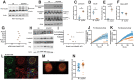
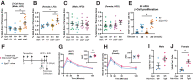
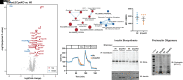
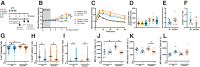
Carboxypeptidase E (CPE) facilitates the conversion of prohormones into mature hormones and is highly expressed in multiple neuroendocrine tissues. Carriers of CPE mutations have elevated plasma proinsulin and develop severe obesity and hyperglycemia. We aimed to determine whether loss of Cpe in pancreatic β-cells disrupts proinsulin processing and accelerates development of diabetes and obesity in mice. Pancreatic β-cell-specific Cpe knockout mice (βCpeKO; Cpefl/fl x Ins1Cre/+) lack mature insulin granules and have elevated proinsulin in plasma; however, glucose-and KCl-stimulated insulin secretion in βCpeKO islets remained intact. High-fat diet-fed βCpeKO mice showed weight gain and glucose tolerance comparable with those of Wt littermates. Notably, β-cell area was increased in chow-fed βCpeKO mice and β-cell replication was elevated in βCpeKO islets. Transcriptomic analysis of βCpeKO β-cells revealed elevated glycolysis and Hif1α-target gene expression. On high glucose challenge, β-cells from βCpeKO mice showed reduced mitochondrial membrane potential, increased reactive oxygen species, reduced MafA, and elevated Aldh1a3 transcript levels. Following multiple low-dose streptozotocin injections, βCpeKO mice had accelerated development of hyperglycemia with reduced β-cell insulin and Glut2 expression. These findings suggest that Cpe and proper proinsulin processing are critical in maintaining β-cell function during the development of hyperglycemia.
Article highlights: Carboxypeptidase E (Cpe) is an enzyme that removes the carboxy-terminal arginine and lysine residues from peptide precursors. Mutations in CPE lead to obesity and type 2 diabetes in humans, and whole-body Cpe knockout or mutant mice are obese and hyperglycemic and fail to convert proinsulin to insulin. We show that β-cell-specific Cpe deletion in mice (βCpeKO) does not lead to the development of obesity or hyperglycemia, even after prolonged high-fat diet treatment. However, β-cell proliferation rate and β-cell area are increased, and the development of hyperglycemia induced by multiple low-dose streptozotocin injections is accelerated in βCpeKO mice.
© 2023 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Furuta M, Carroll R, Martin S, et al. Incomplete processing of proinsulin to insulin accompanied by elevation of Des-31,32 proinsulin intermediates in islets of mice lacking active PC2. J Biol Chem 1998;273:3431–3437 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

