Discovery of ecnoglutide - A novel, long-acting, cAMP-biased glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog
- PMID: 37364710
- PMCID: PMC10339203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101762
Discovery of ecnoglutide - A novel, long-acting, cAMP-biased glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog
Abstract
Objective: Glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 is an incretin hormone that acts after food intake to stimulate insulin production, enhance satiety, and promote weight loss. Here we describe the discovery and characterization of ecnoglutide (XW003), a novel GLP-1 analog.
Methods: We engineered a series of GLP-1 peptide analogs with an alanine to valine substitution (Ala8Val) and a γGlu-2xAEEA linked C18 diacid fatty acid at various positions. Ecnoglutide was selected and characterized in GLP-1 receptor signaling assays in vitro, as well as in db/db mice and a diet induced obese (DIO) rat model. A Phase 1, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, single (SAD) and multiple ascending dose (MAD) study was conducted to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of subcutaneous ecnoglutide injection in healthy participants. SAD doses ranged from 0.03 to 1.0 mg; MAD doses ranged from 0.2 to 0.6 mg once weekly for 6 weeks (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04389775).
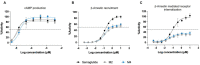
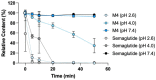
Results: In vitro, ecnoglutide potently induced cAMP (EC50 = 0.018 nM) but not GLP-1 receptor internalization (EC50 > 10 μM), suggesting a desirable signaling bias. In rodent models, ecnoglutide significantly reduced blood glucose, promoted insulin induction, and led to more pronounced body weight reduction compared to semaglutide. In a Phase 1 trial, ecnoglutide was generally safe and well tolerated as a once-weekly injection for up to 6 weeks. Adverse events included decreased appetite, nausea, and headache. The half-life at steady state ranged from 124 to 138 h, supporting once-weekly dosing.
Conclusions: Ecnoglutide showed a favorable potency, pharmacokinetic, and tolerability profile, as well as a simplified manufacturing process. These results support the continued development of ecnoglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Keywords: Ecnoglutide; Glucagon-like peptide-1; Obesity; Peptide analog; Phase 1; Type 2 diabetes; XW003.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest WG, HZ, YL, JF, ZZ, QZ, RZ, BW, YL, SH, HQ, CLJ, EA, LT, MF, WZ, MKJ, SX, and HP are, or were at the time the work was conducted, employees of Sciwind Biosciences.
Figures


References
-
- Eng J., Kleinman W.A., Singh L., Singh G., Raufman J.P. Isolation and characterization of exendin-4, an exendin-3 analogue, from Heloderma suspectum venom. Further evidence for an exendin receptor on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:7402–7405. - PubMed
-
- Østergaard L., Frandsen C.S., Madsbad S. Treatment potential of the GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016;9:241–265. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B., Masmiquel L., Kumar H., Sargin M., Karsbøl J.D., Jacobsen S.H., et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily sitagliptin as an add-on to metformin, thiazolidinediones, or both, in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 2): a 56-week, double-blind, phase 3a, randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:341–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

