Analysis of inflammatory protein profiles in the circulation of COVID-19 patients identifies patients with severe disease phenotypes
- PMID: 37364721
- PMCID: PMC10290733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmed.2023.107331
Analysis of inflammatory protein profiles in the circulation of COVID-19 patients identifies patients with severe disease phenotypes
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) can present with a broad range of clinical manifestations, ranging from asymptomatic to severe multiple organ failure. The severity of the disease can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, and pre-existing medical conditions. Despite multiple efforts to identify reliable prognostic factors and biomarkers, the predictive capacity of these markers for clinical outcomes remains poor. Circulating proteins, which reflect the active mechanisms in an individual, can be easily measured in clinical practice and therefore may be useful as biomarkers for COVID-19 disease severity. In this study, we sought to identify protein biomarkers and endotypes for COVID-19 severity and evaluate their reproducibility in an independent cohort.
Methods: We investigated a cohort of 153 Greek patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in which plasma protein levels were measured using the Olink Explore 1536 panel, which consists of 1472 proteins. We compared the protein profiles from severe and moderate COVID-19 patients to identify proteins associated with disease severity. To evaluate the reproducibility of our findings, we compared the protein profiles of 174 patients with comparable COVID-19 severities in a US COVID-19 cohort to identify proteins consistently correlated with COVID-19 severity in both groups.
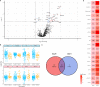
Results: We identified 218 differentially regulated proteins associated with severity, 20 proteins were also replicated in an external cohort which we used for validation. Moreover, we performed unsupervised clustering of patients based on 97 proteins with the highest log2 fold changes in order to identify COVID-19 endotypes. Clustering of patients based on differentially regulated proteins revealed the presence of three clinical endotypes. While endotypes 2 and 3 were enriched for severe COVID-19 patients, endotypes 3 represented the most severe form of the disease.
Conclusions: These results suggest that identified circulating proteins may be useful for identifying COVID-19 patients with worse outcomes, and this potential utility may extend to other populations.
Trial registration: NCT04357366.
Keywords: Biomarker; COVID-19; Clustering; Cytokine; Endotypes; Proteomics.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Magdy Beshbishy A., Oti V.B., Hussein D.E., Rehan I.F., Adeyemi O.S., Rivero-Perez N., Zaragoza-Bastida A., Shah M.A., Abouelezz K., Hetta H.F., Cruz-Martins N., Batiha G.E.S. Factors behind the higher COVID-19 risk in diabetes: a critical review. Front. Public Health. 2021;9:637. doi: 10.3389/FPUBH.2021.591982/BIBTEX. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mathur R., Rentsch C.T., Morton C.E., Hulme W.J., Schultze A., MacKenna B., Eggo R.M., Bhaskaran K., Wong A.Y.S., Williamson E.J., Forbes H., Wing K., McDonald H.I., Bates C., Bacon S., Walker A.J., Evans D., Inglesby P., Mehrkar A., Curtis H.J., DeVito N.J., Croker R., Drysdale H., Cockburn J., Parry J., Hester F., Harper S., Douglas I.J., Tomlinson L., Evans S.J.W., Grieve R., Harrison D., Rowan K., Khunti K., Chaturvedi N., Smeeth L., Goldacre B. Ethnic differences in SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19-related hospitalisation, intensive care unit admission, and death in 17 million adults in England: an observational cohort study using the OpenSAFELY platform. Lancet (London, England) 2021;397:1711. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00634-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sze S., Pan D., Nevill C.R., Gray L.J., Martin C.A., Nazareth J., Minhas J.S., Divall P., Khunti K., Abrams K.R., Nellums L.B., Pareek M. Ethnicity and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;29–30 doi: 10.1016/J.ECLINM.2020.100630. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

