Identification of genomic loci regulating platelet plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in mice
- PMID: 37364776
- PMCID: PMC10826891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtha.2023.06.018
Identification of genomic loci regulating platelet plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in mice
Abstract
Background: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1, Serpine1) is an important circulating fibrinolysis inhibitor. PAI-1 exists in 2 pools, packaged within platelet α-granules and freely circulating in plasma. Elevated plasma PAI-1 levels are associated with cardiovascular disease. However, little is known about the regulation of platelet PAI-1 (pPAI-1).
Objectives: We investigated the genetic control of pPAI-1 levels in mice and humans.
Methods: We measured pPAI-1 antigen levels via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in platelets isolated from 10 inbred mouse strains, including LEWES/EiJ (LEWES) and C57BL/6J (B6). LEWES and B6 were crossed to produce the F1 generation, B6LEWESF1. B6LEWESF1 mice were intercrossed to produce B6LEWESF2 mice. These mice were subjected to genome-wide genetic marker genotyping followed by quantitative trait locus analysis to identify pPAI-1 regulatory loci.
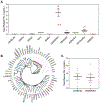
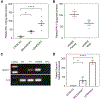
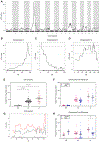
Results: We identified differences in pPAI-1 between several laboratory strains, with LEWES having pPAI-1 levels more than 10-fold higher than those in B6. Quantitative trait locus analysis of B6LEWESF2 offspring identified a major pPAI-1 regulatory locus on chromosome 5 from 136.1 to 137.6 Mb (logarithm of the odds score, 16.2). Significant pPAI-1 modifier loci on chromosomes 6 and 13 were also identified.
Conclusion: Identification of pPAI-1 genomic regulatory elements provides insights into platelet/megakaryocyte-specific and cell type-specific gene expression. This information can be used to design more precise therapeutic targets for diseases where PAI-1 plays a role.
Keywords: blood platelets; fibrinolysis; gene expression regulation; megakaryocytes; quantitative trait loci; serpin E1.
Copyright © 2023 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interests There are no competing interests to disclose.
Figures
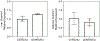
References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2021 Update A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(8):e254–e743. - PubMed
-
- Westrick RJ, Eitzman DT. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in vascular thrombosis. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8(9):966–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

