A Cre Driver Line for Genetic Targeting of Kappa Opioid Receptor Expressing Cells
- PMID: 37364995
- PMCID: PMC10348446
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0043-23.2023
A Cre Driver Line for Genetic Targeting of Kappa Opioid Receptor Expressing Cells
Abstract
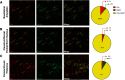
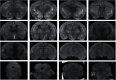
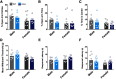
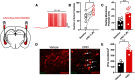
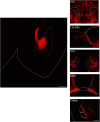
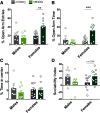
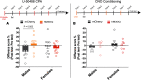
Here we describe the generation and characterization of a Cre knock-in mouse line that harbors a Cre insertion in the 3'UTR of the κ opioid receptor gene (Oprk1) locus and provides genetic access to populations of κ opioid receptor (KOR)-expressing neurons throughout the brain. Using a combination of techniques including RNA in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry, we report that Cre is expressed with high fidelity in KOR-expressing cells throughout the brain in this mouse line. We also provide evidence that Cre insertion does not alter basal KOR function. Baseline anxiety-like behaviors and nociceptive thresholds are unaltered in Oprk1-Cre mice. Chemogenetic activation of KOR-expressing cells in the basolateral amygdala (BLAKOR cells) resulted in several sex-specific effects on anxiety-like and aversive behaviors. Activation led to decreased anxiety-like behavior on the elevated plus maze and increased sociability in female but not in male Oprk1-Cre mice. Activation of BLAKOR cells also attenuated KOR agonist-induced conditioned place aversion (CPA) in male Oprk1-Cre mice. Overall, these results suggest a potential role for BLAKOR cells in regulating anxiety-like behaviors and KOR-agonist mediated CPA. In summary, these results provide evidence for the utility of the newly generated Oprk1-Cre mice in assessing localization, anatomy, and function of KOR circuits throughout the brain.
Keywords: anxiety; conditioned place aversion; dynorphin; genetic access; knock-in mice; social interaction.
Copyright © 2023 Paliarin et al.
Figures
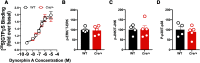
Similar articles
-
Kappa Opioid Receptor-Induced Aversion Requires p38 MAPK Activation in VTA Dopamine Neurons.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 16;35(37):12917-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2444-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26377476 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a KOR-Cre knockin mouse strain to study cells involved in kappa opioid signaling.Genesis. 2016 Jan;54(1):29-37. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22910. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Genesis. 2016. PMID: 26575788 Free PMC article.
-
Kappa opioid receptors on dopaminergic neurons are necessary for kappa-mediated place aversion.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Dec;38(13):2623-31. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.171. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23921954 Free PMC article.
-
Dopaminergic cellular and circuit contributions to kappa opioid receptor mediated aversion.Neurochem Int. 2019 Oct;129:104504. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.104504. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Neurochem Int. 2019. PMID: 31301327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor system regulation on amygdaloid circuitry: Implications for neuropsychiatric disorders.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 Oct 5;16:963691. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2022.963691. eCollection 2022. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36276608 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Dynorphin/-Opioid Receptor System at the Interface of Hyperalgesia/Hyperkatifeia and Addiction.Curr Addict Rep. 2025;12(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s40429-025-00618-x. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Curr Addict Rep. 2025. PMID: 40124896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Projection-Targeted Photopharmacology Reveals Distinct Anxiolytic Roles for Presynaptic mGluR2 in Prefrontal- and Insula-Amygdala Synapses.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 16:2024.01.15.575699. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.15.575699. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Neuron. 2025 Mar 19;113(6):912-930.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2025.01.002. PMID: 38293136 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Projection-targeted photopharmacology reveals distinct anxiolytic roles for presynaptic mGluR2 in prefrontal- and insula-amygdala synapses.Neuron. 2025 Mar 19;113(6):912-930.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2025.01.002. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Neuron. 2025. PMID: 39879977
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
