Bone dysplasia in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome is associated with dysregulated differentiation and function of bone cell populations
- PMID: 37365004
- PMCID: PMC10497813
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13903
Bone dysplasia in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome is associated with dysregulated differentiation and function of bone cell populations
Abstract
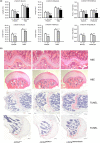
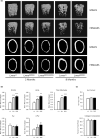
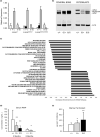
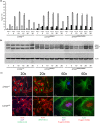
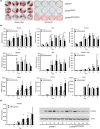
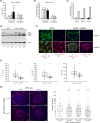
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) is a premature aging disorder affecting tissues of mesenchymal origin. Most individuals with HGPS harbor a de novo c.1824C > T (p.G608G) mutation in the gene encoding lamin A (LMNA), which activates a cryptic splice donor site resulting in production of the toxic "progerin" protein. Clinical manifestations include growth deficiency, lipodystrophy, sclerotic dermis, cardiovascular defects, and bone dysplasia. Here we utilized the LmnaG609G knock-in (KI) mouse model of HGPS to further define mechanisms of bone loss associated with normal and premature aging disorders. Newborn skeletal staining of KI mice revealed altered rib cage shape and spinal curvature, and delayed calvarial mineralization with increased craniofacial and mandibular cartilage content. MicroCT analysis and mechanical testing of adult femurs indicated increased fragility associated with reduced bone mass, recapitulating the progressive bone deterioration that occurs in HGPS patients. We investigated mechanisms of bone loss in KI mice at the cellular level in bone cell populations. Formation of wild-type and KI osteoclasts from marrow-derived precursors was inhibited by KI osteoblast-conditioned media in vitro, suggesting a secreted factor(s) responsible for decreased osteoclasts on KI trabecular surfaces in vivo. Cultured KI osteoblasts exhibited abnormal differentiation characterized by reduced deposition and mineralization of extracellular matrix with increased lipid accumulation compared to wild-type, providing a mechanism for altered bone formation. Furthermore, quantitative analyses of KI transcripts confirmed upregulation of adipogenic genes both in vitro and in vivo. Thus, osteoblast phenotypic plasticity, inflammation and altered cellular cross-talk contribute to abnormal bone formation in HGPS mice.
Keywords: Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome; bone dysplasia; lamin A/C; osteoblasts; osteoclasts.
© 2023 The Authors. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Akhter, M. P. , Lappe, J. M. , Davies, K. M. , & Recker, R. R. (2007). Transmenopausal changes in the trabecular bone structure. Bone, 41, 111–116. - PubMed
-
- Akter, R. , Rivas, D. , Geneau, G. , Drissi, H. , & Duque, G. (2009). Effect of lamin a/C knockdown on osteoblast differentiation and function. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 24, 283–293. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosi, T. H. , Marecic, O. , McArdle, A. , Sinha, R. , Gulati, G. S. , Tong, X. , Wang, Y. , Steininger, H. M. , Hoover, M. Y. , Koepke, L. S. , Murphy, M. P. , Sokol, J. , Seo, E. Y. , Tevlin, R. , Lopez, M. , Brewer, R. E. , Mascharak, S. , Lu, L. , Ajanaku, O. , … Chan, C. K. F. (2021). Aged skeletal stem cells generate an inflammatory degenerative niche. Nature, 597, 256–262. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergo, M. O. , Gavino, B. , Ross, J. , Schmidt, W. K. , Hong, C. , Kendall, L. V. , Mohr, A. , Meta, M. , Genant, H. , Jiang, Y. , Wisner, E. R. , van Bruggen, N. , Carano, R. A. , Michaelis, S. , Griffey, S. M. , & Young, S. G. (2002). Zmpste24 deficiency in mice causes spontaneous bone fractures, muscle weakness, and a prelamin a processing defect. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99, 13049–13054. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

