Altered gray-to-white matter tissue contrast in preterm-born adults
- PMID: 37365964
- PMCID: PMC10580354
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.14320
Altered gray-to-white matter tissue contrast in preterm-born adults
Abstract
Aims: To investigate cortical organization in brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of preterm-born adults using percent contrast of gray-to-white matter signal intensities (GWPC), which is an in vivo proxy measure for cortical microstructure.
Methods: Using structural MRI, we analyzed GWPC at different percentile fractions across the cortex (0%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, and 60%) in a large and prospectively collected cohort of 86 very preterm-born (<32 weeks of gestation and/or birth weight <1500 g, VP/VLBW) adults and 103 full-term controls at 26 years of age. Cognitive performance was assessed by full-scale intelligence quotient (IQ) using the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale.
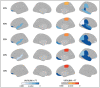
Results: GWPC was significantly decreased in VP/VLBW adults in frontal, parietal, and temporal associative cortices, predominantly in the right hemisphere. Differences were pronounced at 20%, 30%, and 40%, hence, in middle cortical layers. GWPC was significantly increased in right paracentral lobule in VP/VLBW adults. GWPC in frontal and temporal cortices was positively correlated with birth weight, and negatively with duration of ventilation (p < 0.05). Furthermore, GWPC in right paracentral lobule was negatively correlated with IQ (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Widespread aberrant gray-to-white matter contrast suggests lastingly altered cortical microstructure after preterm birth, mainly in middle cortical layers, with differential effects on associative and primary cortices.
Keywords: brain development; cerebral cortex; preterm birth; structural magnetic resonance imaging; tissue contrast.
© 2023 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nosarti C, Al‐Asady MHS, Frangou S, Stewart AL, Rifkin L, Murray RM. Adolescents who were born very preterm have decreased brain volumes. Brain. 2002;125(Pt 7):1616‐1623. - PubMed
-
- Skranes J, Vangberg TR, Kulseng S, et al. Clinical findings and white matter abnormalities seen on diffusion tensor imaging in adolescents with very low birth weight. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 3):654‐666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

