The Role of mTOR Inhibitors after Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 37366904
- PMCID: PMC10297627
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol30060421
The Role of mTOR Inhibitors after Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
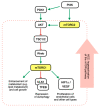
Liver transplantation is a treatment option for nonresectable patients with early-stage HCC, with more significant advantages when Milan criteria are fulfilled. An immunosuppressive regimen is required to reduce the risk of graft rejection after transplantation, and CNIs represent the drugs of choice in this setting. However, their inhibitory effect on T-cell activity accounts for a higher risk of tumour regrowth. mTOR inhibitors (mTORi) have been introduced as an alternative immunosuppressive approach to conventional CNI-based regimens to address both immunosuppression and cancer control. The PI3K-AKT-mTOR signalling pathway regulates protein translation, cell growth, and metabolism, and the pathway is frequently deregulated in human tumours. Several studies have suggested the role of mTORi in reducing HCC progression after LT, accounting for a lower recurrence rate. Furthermore, mTOR immunosuppression controls the renal damage associated with CNI exposure. Conversion to mTOR inhibitors is associated with stabilizing and recovering renal dysfunction, suggesting an essential renoprotective effect. Limitations in this therapeutic approach are related to their negative impact on lipid and glucose metabolism as well as on proteinuria development and wound healing. This review aims to summarize the roles of mTORi in managing patients with HCC undergoing LT. Strategies to overcome common adverse effects are also proposed.
Keywords: HCC; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunosuppression; liver transplantation; mTOR; mTOR inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of mTOR Inhibitors in Pediatric Liver Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review.Paediatr Drugs. 2024 Nov;26(6):673-693. doi: 10.1007/s40272-024-00648-4. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Paediatr Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39251556
-
Long-Term Renal Function in Liver Transplant Recipients After Conversion From Calcineurin Inhibitors to mTOR Inhibitors.Ann Transplant. 2015 Nov 26;20:707-13. doi: 10.12659/aot.895320. Ann Transplant. 2015. PMID: 26608590
-
Immunosuppressive Treatment With mTOR Inhibitors for Malignancies After Liver Transplantation: Long-Term Survival Retrospective Analysis.Transplant Proc. 2020 Jun;52(5):1507-1510. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.02.058. Epub 2020 Mar 22. Transplant Proc. 2020. PMID: 32213292
-
A prospective randomised, open-labeled, trial comparing sirolimus-containing versus mTOR-inhibitor-free immunosuppression in patients undergoing liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2010 May 11;10:190. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-190. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20459775 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
mTORi-based immunosuppression reduces HCC recurrence at the expense of increased adverse side effects: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Transplant. 2022 Dec;36(12):e14823. doi: 10.1111/ctr.14823. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Clin Transplant. 2022. PMID: 36124430
Cited by
-
Prevention of liver cancer in the era of next-generation antivirals and obesity epidemic.Hepatology. 2025 Jan 14:10.1097/HEP.0000000000001227. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001227. Online ahead of print. Hepatology. 2025. PMID: 39808821 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR inhibitor reduces nontumour-related death in liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Biomed. 2024 Mar 10;5(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00170-6. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38461206 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance immunosuppressive therapy in liver transplantation: results from CESIT study, an Italian retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2024 Nov 12;14(11):e087373. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-087373. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39532354 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Approach to Post-Transplant Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Certainties and Open Issues.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 26;15(23):5593. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235593. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The long-term effects of multidrug immunosuppressive protocols based on calcineurin inhibitors and conversion to rapamycin on the morphology, apoptosis, and proliferation of rat salivary glands.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Oct;75(5):1240-1253. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00521-0. Epub 2023 Sep 2. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37658979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam R., Karam V., Delvart V., O’Grady J., Mirza D., Klempnauer J., Castaing D., Neuhaus P., Jamieson N., Salizzoni M., et al. Evolution of indications and results of liver transplantation in Europe. A report from the European Liver Transplant Registry (ELTR) J. Hepatol. 2012;57:675–688. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.04.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

