A Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay Based on Biotinylated Nanobody and Streptavidin Amplification for Diazinon Sensitive Quantification
- PMID: 37366942
- PMCID: PMC10296574
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13060577
A Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay Based on Biotinylated Nanobody and Streptavidin Amplification for Diazinon Sensitive Quantification
Abstract
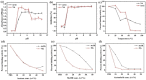
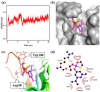
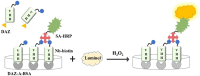
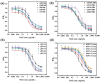
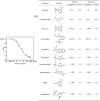
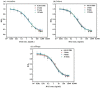
The advantages of genetic modification and preferable physicochemical qualities make nanobody (Nb) easy to develop a sensitive and stable immunosensor platform. Herein, an indirect competitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (ic-CLEIA) based on biotinylated Nb was established for the quantification of diazinon (DAZ). The anti-DAZ Nb, named Nb-EQ1, with good sensitivity and specificity, was obtained from an immunized library via a phage display technique, where the molecular docking results indicated that the hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interactions between DAZ and complementarity-determining region 3 and framework region 2 in Nb-EQ1 played a critical role in the Nb-DAZ affinity processes. Subsequently, the Nb-EQ1 was further biotinylated to generate a bi-functional Nb-biotin, and then an ic-CLEIA was developed for DAZ determination via signal amplification of the biotin-streptavidin platform. The results showed that the proposed method based on Nb-biotin had a high specificity and sensitivity to DAZ, with a relative broader linear range of 0.12-25.96 ng/mL. After being 2-folds dilution of the vegetable samples matrix, the average recoveries were 85.7-113.9% with a coefficient of variation of 4.2-19.2%. Moreover, the results for the analysis of real samples by the developed ic-CLEIA correlated well with that obtained by reference method GC-MS (R2 ≥ 0.97). In summary, the ic-CLEIA based on biotinylated Nb-EQ1 and streptavidin recognition demonstrated itself to be a convenient tool for the quantification of DAZ in vegetables.
Keywords: diazinon; indirect competitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay; nanobody; phage display; signal amplification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of a biotin-streptavidin-amplified nanobody-based ELISA for ochratoxin A in cereal.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Apr 30;171:382-388. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.103. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019. PMID: 30616155
-
Streptavidin-biotin-based directional double Nanobody sandwich ELISA for clinical rapid and sensitive detection of influenza H5N1.J Transl Med. 2014 Dec 20;12:352. doi: 10.1186/s12967-014-0352-5. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25526777 Free PMC article.
-
Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay and Bioluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay for Tenuazonic Acid Mycotoxin by Exploitation of Nanobody and Nanobody-Nanoluciferase Fusion.Anal Chem. 2020 Sep 1;92(17):11935-11942. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02338. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Anal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32702970 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobody-based magnetic chemiluminescence immunoassay for one-pot detection of ochratoxin A.Talanta. 2023 Jun 1;258:124388. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124388. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 36921368
-
Biotin interference in immunoassays based on biotin-strept(avidin) chemistry: An emerging threat.Biotechnol Adv. 2019 Sep-Oct;37(5):634-641. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Biotechnol Adv. 2019. PMID: 30872068 Review.
References
-
- Yao J., Wang Z., Guo L., Xu X., Liu L., Xu L., Song S., Xu C., Kuang H. Advances in immunoassays for organophosphorus and pyrethroid pesticides. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020;131:116022. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.116022. - DOI
-
- Lai X., Lv X., Zhang G., Xiong Z., Lai W., Peng J. Highly Specific Anti-tylosin Monoclonal Antibody and Its Application in the Quantum Dot Bead-Based Immunochromatographic Assay. Food Anal. Methods. 2020;13:2258–2268. doi: 10.1007/s12161-020-01846-9. - DOI
-
- Becheva Z.R., Atanasova M.K., Ivanov Y.L., Godjevargova T.I. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Fluorescence Immunoassay for Determination of Ochratoxin A in Milk. Food Anal. Methods. 2020;13:2238–2248. doi: 10.1007/s12161-020-01848-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

