Low Overpotential Amperometric Sensor Using Yb2O3.CuO@rGO Nanocomposite for Sensitive Detection of Ascorbic Acid in Real Samples
- PMID: 37366953
- PMCID: PMC10295996
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13060588
Low Overpotential Amperometric Sensor Using Yb2O3.CuO@rGO Nanocomposite for Sensitive Detection of Ascorbic Acid in Real Samples
Abstract
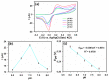
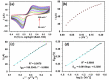
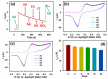
The ultimate objective of this research work is to design a sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor for the efficient detection of ascorbic acid (AA), a vital antioxidant found in blood serum that may serve as a biomarker for oxidative stress. To achieve this, we utilized a novel Yb2O3.CuO@rGO nanocomposite (NC) as the active material to modify the glassy carbon working electrode (GCE). The structural properties and morphological characteristics of the Yb2O3.CuO@rGO NC were investigated using various techniques to ensure their suitability for the sensor. The resulting sensor electrode was able to detect a broad range of AA concentrations (0.5-1571 µM) in neutral phosphate buffer solution, with a high sensitivity of 0.4341 µAµM-1cm-2 and a reasonable detection limit of 0.062 µM. The sensor's great sensitivity and selectivity allowed it to accurately determine the levels of AA in human blood serum and commercial vitamin C tablets. It demonstrated high levels of reproducibility, repeatability, and stability, making it a reliable and robust sensor for the measurement of AA at low overpotential. Overall, the Yb2O3.CuO@rGO/GCE sensor showed great potential in detecting AA from real samples.
Keywords: Yb2O3.CuO@rGO; amperometric sensor; ascorbic acid; human blood serum; vitamin C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Fabrications of the Flexible Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Using Au-CuO-rGO and Au-CuO-rGO-MWCNTs Nanocomposites as Carriers.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 22;23(19):8029. doi: 10.3390/s23198029. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37836858 Free PMC article.
-
CeO2·ZnO@biomass-derived carbon nanocomposite-based electrochemical sensor for efficient detection of ascorbic acid.Anal Biochem. 2024 Sep;692:115574. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2024.115574. Epub 2024 May 22. Anal Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38782251
-
Simultaneous and individual determination of seven biochemical species using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite of Pt nanoparticle and graphene by a one-step electrochemical process.Talanta. 2022 Sep 1;247:123590. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123590. Epub 2022 May 26. Talanta. 2022. PMID: 35653858
-
Preparation of Cu₂O-Reduced Graphene Nanocomposite Modified Electrodes towards Ultrasensitive Dopamine Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Jan 12;18(1):199. doi: 10.3390/s18010199. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29329206 Free PMC article.
-
The facile and simple synthesis of poly(3,4ethylenedioxythiophene) anchored reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for biochemical analysis.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Oct 24;1077:150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.053. Epub 2019 May 24. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31307704
Cited by
-
Fabrications of the Flexible Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Using Au-CuO-rGO and Au-CuO-rGO-MWCNTs Nanocomposites as Carriers.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 22;23(19):8029. doi: 10.3390/s23198029. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37836858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qu C., Li H., Zhou S., Li G., Wang C., Snyders R., Bittencourt C., Li W. Bi2S3/RGO Composite Based Electrochemical Sensor for Ascorbic Acid Detection. Chemosensors. 2021;9:190. doi: 10.3390/chemosensors9080190. - DOI
-
- Tkachenko A.B., Onizhuk M.O., Tkachenko O.S., Arenas L.T., Benvenutti E.V., Gushikem Y., Panteleimonov A.V. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Graphite Electrode Modified with Silica Containing 1-n-Propyl-3-Methylimidazolium Species for Determination of Ascorbic Acid. Methods Objects Chem. Anal. 2019;14:5–14. doi: 10.17721/moca.2019.5-14. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

