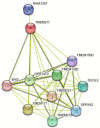
TMEM211 Promotes Tumor Progression and Metastasis in Colon Cancer
- PMID: 37367036
- PMCID: PMC10297151
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45060287
TMEM211 Promotes Tumor Progression and Metastasis in Colon Cancer
Abstract
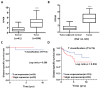
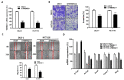
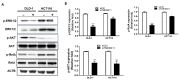
Colon cancer is the third most important cancer type, leading to a remarkable number of deaths, indicating the necessity of new biomarkers and therapeutic targets for colon cancer patients. Several transmembrane proteins (TMEMs) are associated with tumor progression and cancer malignancy. However, the clinical significance and biological roles of TMEM211 in cancer, especially in colon cancer, are still unknown. In this study, we found that TMEM211 was highly expressed in tumor tissues and the increased TMEM211 was associated with poor prognosis in colon cancer patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. We also showed that abilities regarding migration and invasion were reduced in TMEM211-silenced colon cancer cells (HCT116 and DLD-1). Moreover, TMEM211-silenced colon cancer cells showed decreased levels of Twist1, N-cadherin, Snail and Slug but increased levels of E-cadherin. Levels of phosphorylated ERK, AKT and RelA (NF-κB p65) were also decreased in TMEM211-silenced colon cancer cells. Our findings indicate that TMEM211 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition for metastasis through coactivating the ERK, AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways, which might provide a potential prognostic biomarker or therapeutic target for colon cancer patients in the future.
Keywords: colon cancer; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; prognosis; signaling pathways; transmembrane protein 211.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrin-linked kinase overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via nuclear factor-κB signaling in colorectal cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 21;22(15):3969-77. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.3969. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27099440 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NF-κB by the RANKL/RANK system up-regulates snail and twist expressions and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mammary tumor cell lines.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 5;32(1):62. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-32-62. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24011086 Free PMC article.
-
AKR1B10 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and migration via the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Biosci. 2021 Aug 21;11(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00677-3. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34419144 Free PMC article.
-
The novel role of Yin Yang 1 in the regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer via the dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/YY1/RKIP/PTEN Circuitry.Crit Rev Oncog. 2011;16(3-4):211-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i3-4.50. Crit Rev Oncog. 2011. PMID: 22248055 Review.
-
The emerging role of transmembrane proteins in tumorigenesis and therapy.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):1447-1466. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1660. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40104699 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The feasible role of soluble E‑cadherin in spheroidogenesis of HCT116 colorectal cancer cells, a candidate biomarker for liquid biopsy.Oncol Lett. 2025 Mar 24;29(5):245. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14991. eCollection 2025 May. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40182609 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

