DDIT4 Downregulation by siRNA Approach Increases the Activity of Proteins Regulating Fatty Acid Metabolism upon Aspirin Treatment in Human Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 37367045
- PMCID: PMC10297095
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45060296
DDIT4 Downregulation by siRNA Approach Increases the Activity of Proteins Regulating Fatty Acid Metabolism upon Aspirin Treatment in Human Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
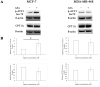
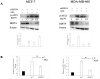
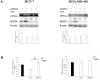
Repositioning of aspirin for a more effective breast cancer (BC) treatment requires identification of predictive biomarkers. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the anticancer activity of aspirin remains fully undefined. Cancer cells enhance de novo fatty acid (FA) synthesis and FA oxidation to maintain a malignant phenotype, and the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTORC1) is required for lipogenesis. We, therefore, aimed to test if the expression of mTORC1 suppressor DNA damage-inducible transcript (DDIT4) affects the activity of main enzymes in FA metabolism after aspirin treatment. MCF-7 and MDA-MB-468 human BC cell lines were transfected with siRNA to downregulate DDIT4. The expression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 A (CPT1A) and serine 79-phosphorylated acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1) were analyzed by Western Blotting. Aspirin enhanced ACC1 phosphorylation by two-fold in MCF-7 cells and had no effect in MDA-MB-468 cells. Aspirin did not change the expression of CPT1A in either cell line. We have recently reported DDIT4 itself to be upregulated by aspirin. DDIT4 knockdown resulted in 1.5-fold decreased ACC1 phosphorylation (dephosphorylation activates the enzyme), 2-fold increased CPT1A expression in MCF-7 cells, and 2.8-fold reduced phosphorylation of ACC1 following aspirin exposure in MDA-MB-468 cells. Thus, DDIT4 downregulation raised the activity of main lipid metabolism enzymes upon aspirin exposure which is an undesired effect as FA synthesis and oxidation are linked to malignant phenotype. This finding may be clinically relevant as DDIT4 expression has been shown to vary in breast tumors. Our findings justify further, more extensive investigation of the role of DDIT4 in aspirin's effect on fatty acid metabolism in BC cells.
Keywords: ACC1; CPT1A; DDIT4; aspirin; breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
siRNA Knockdown of REDD1 Facilitates Aspirin-Mediated Dephosphorylation of mTORC1 Target 4E-BP1 in MDA-MB-468 Human Breast Cancer Cell Line.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Feb 5;13:1123-1133. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S264414. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 33574709 Free PMC article.
-
Withania somnifera root extract inhibits fatty acid synthesis in prostate cancer cells.J Tradit Complement Med. 2020 Feb 7;10(3):188-197. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.02.002. eCollection 2020 May. J Tradit Complement Med. 2020. PMID: 32670813 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing a relationship between prolactin and altered fatty acid β-oxidation via carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 in breast cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2011 Feb 4;11:56. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-56. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21294903 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylases and Diseases.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 11;12:836058. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.836058. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35359351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Damage Inducible Transcript 4 Gene: The Switch of the Metabolism as Potential Target in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2018 Apr 12;8:106. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00106. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29707520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drug Repurposing: A Conduit to Unravelling Metabolic Reprogramming for Cancer Treatment.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(8):601-627. doi: 10.2174/0113895575339660250106093738. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39835565 Review.
-
Advanced Molecular Solutions for Cancer Therapy-The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly of the Biomarker Paradigm.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Feb 22;46(3):1694-1699. doi: 10.3390/cimb46030109. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38534725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J.F., Jamieson G.G., Wu T.C., Zhu G.J., Drew P.A. A preliminary study on the postoperative survival of patients given aspirin after resection for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus or adenocarcinoma of the cardia. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009;16:1397–1402. doi: 10.1245/s10434-009-0382-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Staalduinen J., Frouws M., Reimers M., Bastiaannet E., van Herk-Sukel M.P., Lemmens V., de Steur W.O., Hartgrink H.H., van de Velde C.J., Liefers G.J. The effect of aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use after diagnosis on survival of oesophageal cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer. 2016;114:1053–1059. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.65. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

