M2 Macrophages-Derived Exosomal miRNA-23a-3p Promotes the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting PTEN
- PMID: 37367063
- PMCID: PMC10297043
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45060314
M2 Macrophages-Derived Exosomal miRNA-23a-3p Promotes the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting PTEN
Abstract
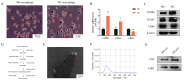
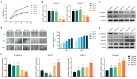
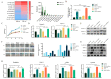
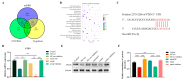
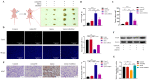
Exosomes from tumor cells and immune cells regulate the tumor microenvironment through the biomolecules or microRNAs (miRNAs) they carry. This research aims to investigate the role of miRNA in exosomes derived from tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). RT-qPCR and Western blotting assays were used to determine the expression of genes and proteins in OSCC cells. CCK-8, Scratch assay and invasion-related proteins were utilized to detect the malignant progression of tumor cells. High-throughput sequencing predicted differentially expressed miRNAs in exosomes secreted by M0 and M2 macrophages. Compared with exosomes from M0 macrophages, exosomes from M2 macrophages led to enhanced proliferation and invasion of OSCC cells and inhibited their apoptosis. High-throughput sequencing results show that miR-23a-3p is differentially expressed in exosomes from M0 and M2 macrophages. MiRNA target gene database predicts that phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) are target genes of miR-23a-3p. Further studies revealed that transfection of miR-23a-3p mimics inhibited PTEN expression in vivo and in vitro and promoted the malignant progression of OSCC cells, which was reversed by miR-23a-3p inhibitors. MiR-23a-3p in exosomes derived from M2 macrophages promotes malignant progression of OSCC. PTEN is a potential intracellular target of miR-23a-3p. MiR-23a-3p, an M2 macrophage-associated exosome, is a promising target for the future treatment of OSCC.
Keywords: M2 macrophages; MiR-23a-3p; OSCC; PTEN; exosome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
M2 macrophage-secreted exosomes promote metastasis and increase vascular permeability in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Oct 30;21(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00872-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37904170 Free PMC article.
-
Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomes promote M2 subtype macrophage polarization mediated by exosome-enclosed miR-29a-3p.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):C731-C740. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00366.2018. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30811223
-
Oleanolic acid inhibits M2 macrophage polarization and potentiates anti-PD-1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-130b-3p-PTEN-PI3K-Akt signaling and glycolysis.Phytomedicine. 2025 Jun;141:156750. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156750. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40250003
-
Role of exosomes in the communication and treatment between OSCC and normal cells.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 20;10(7):e28148. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28148. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38560136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehension of PTEN-Regulated MicroRNA Profiling in Oral Premalignant Lesions: A Critical Link to Early Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cureus. 2025 Apr 16;17(4):e82343. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82343. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40385769 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of exosomes in tumor immunity: recent progresses.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Apr 3;12:1372847. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1372847. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38633106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ESM1 suppresses LncRNA GAS5/miR-23a-3p/PTEN axis to promote the cisplatin-chemotherapy resistance of ovarian cancer cells via activating the PI3K/AKT pathway.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 16;16(1):327. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02113-1. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40089962 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of macrophages in OSCC progression.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 14;15:1517886. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1517886. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39877372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor microenvironment in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1485174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485174. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39744628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal miR‑3681‑3p from M2‑polarized macrophages confers cisplatin resistance to gastric cancer cells by targeting MLH1.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Apr;31(4):94. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13459. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39981936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gan C.P., Sam K.K., Yee P.S., Zainal N.S., Lee B.K.B., Rahman Z.A.A., Patel V., Tan A.C., Zain R.B., Cheong S.C. IFITM3 knockdown reduces the expression of CCND1 and CDK4 and suppresses the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell. Oncol. 2019;42:477–490. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00437-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu M., O’connor R.S., Trefely S., Graham K., Snyder N.W., Beatty G.L. Metabolic rewiring of macrophages by CpG potentiates clearance of cancer cells and overcomes tumor-expressed CD47−mediated ‘don’t-eat-me’ signal. Nat. Immunol. 2020;20:265–275. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0292-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

