Chitosan Hydrogel-Delivered ABE8e Corrects PAX9 Mutant in Dental Pulp Stem Cells
- PMID: 37367107
- PMCID: PMC10297230
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9060436
Chitosan Hydrogel-Delivered ABE8e Corrects PAX9 Mutant in Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Abstract
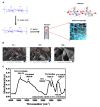
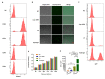
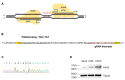
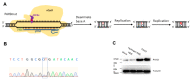
Hypodontia (dental agenesis) is a genetic disorder, and it has been identified that the mutation C175T in PAX9 could lead to hypodontia. Cas9 nickase (nCas9)-mediated homology-directed repair (HDR) and base editing were used for the correction of this mutated point. This study aimed to investigate the effect of HDR and the base editor ABE8e in editing PAX9 mutant. It was found that the chitosan hydrogel was efficient in delivering naked DNA into dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs). To explore the influence of the C175T mutation in PAX9 on the proliferation of DPSCs, hydrogel was employed to deliver PAX9 mutant vector into DPSCs, finding that the PAX9-containing C175T mutation failed to promote the proliferation of DPSCs. Firstly, DPSCs stably carrying PAX9 mutant were constructed. Either an HDR or ABE8e system was delivered into the above-mentioned stable DPSCs, and then the correction efficiency using Sanger sequencing and Western blotting was determined. Meanwhile, the ABE8e presented significantly higher efficiency in correcting C175T compared with HDR. Furthermore, the corrected PAX9 presented enhanced viability and differentiation capacity for osteogenic and neurogenic lineages; the corrected PAX9 even possessed extremely enhanced transcriptional activation ability. In summary, this study has powerful implications for studies into base editors, chitosan hydrogel, and DPSCs in treating hypodontia.
Keywords: ABE8e; PAX9; dental agenesis; dental pulp stem cells; hydrogel; hypodontia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Delivery of Cas9-guided ABE8e into stem cells using poly(l-lysine) polypeptides for correction of the hemophilia-associated FIX missense mutation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Nov 5;628:49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.08.076. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36081278
-
The Role of Interleukin 6 in Osteogenic and Neurogenic Differentiation Potentials of Dental Pulp Stem Cells.J Endod. 2019 Nov;45(11):1342-1348. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2019.08.002. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Endod. 2019. PMID: 31540748
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes human dental pulp stem cells cultured in 3D porous chitosan scaffolds to neural differentiation.Int J Neurosci. 2021 Jul;131(7):625-633. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1744592. Epub 2020 Apr 5. Int J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32186218
-
Evaluation of Chitosan Hydrogel for Sustained Delivery of VEGF for Odontogenic Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Dec 19;2019:1515040. doi: 10.1155/2019/1515040. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 31949434 Free PMC article.
-
PAX9 gene mutations and tooth agenesis: A review.Clin Genet. 2017 Nov;92(5):467-476. doi: 10.1111/cge.12986. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Clin Genet. 2017. PMID: 28155232 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of action and potential therapeutic targets of TGF-β-related signaling pathway and its downstream miRNA expression in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1596767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1596767. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40548051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sacks D., Baxter B., Campbell B.C.V., Carpenter J.S., Cognard C., Dippel D., Eesa M., Fischer U., Hausegger K., Hirsch J.A., et al. Multisociety Consensus Quality Improvement Revised Consensus Statement for Endovascular Therapy of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Stroke. 2018;13:612–632. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2017.11.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhol C.S., Patil S., Sahu B.B., Patra S.K., Bhutia S.K. The clinical significance and correlative signaling pathways of paired box gene 9 in development and carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer. 2021;1876:188561. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

