Synthesis and Characterisation of Hydrogels Based on Poly (N-Vinylcaprolactam) with Diethylene Glycol Diacrylate
- PMID: 37367110
- PMCID: PMC10298195
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9060439
Synthesis and Characterisation of Hydrogels Based on Poly (N-Vinylcaprolactam) with Diethylene Glycol Diacrylate
Abstract
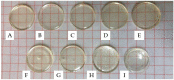
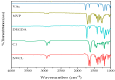
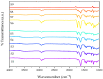
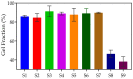
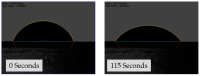
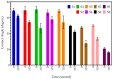
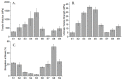
Poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) is a polymer that is biocompatible, water-soluble, thermally sensitive, non-toxic, and nonionic. In this study, the preparation of hydrogels based on Poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) with diethylene glycol diacrylate is presented. The N-Vinylcaprolactam-based hydrogels are synthesised by using a photopolymerisation technique using diethylene glycol diacrylate as a crosslinking agent, and Diphenyl (2, 4, 6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide as a photoinitiator. The structure of the polymers is investigated via Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. The polymers are further characterised using differential scanning calorimetry and swelling analysis. This study is conducted to determine the characteristics of P (N-vinylcaprolactam) with diethylene glycol diacrylate, including the addition of Vinylacetate or N-Vinylpyrrolidone, and to examine the effects on the phase transition. Although various methods of free-radical polymerisation have synthesised the homopolymer, this is the first study to report the synthesis of Poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) with diethylene glycol diacrylate by using free-radical photopolymerisation, using Diphenyl (2, 4, 6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide to initiate the reaction. FTIR analysis shows that the NVCL-based copolymers are successfully polymerised through UV photopolymerisation. DSC analysis indicates that increasing the concentration of crosslinker results in a decrease in the glass transition temperature. Swelling analysis displays that the lower the concentration of crosslinker present in the hydrogel, the quicker the hydrogels reach their maximum swelling ratio.
Keywords: N-vinylcaprolactam; copolymers; hydrogel; photopolymerisation; swelling behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Bahram M., Mohseni N. An Introduction to Hydrogels and Some Recent Applications. IntechOpen; New York, NY, USA: 2016.
-
- Sun A., He X., Ji X., Hu D., Pan M., Zhang M., Qian Z. Current research progress of photopolymerized hydrogels in tissue engineering. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2021;32:2117–2126. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.01.048. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

