Rheological Considerations of Pharmaceutical Formulations: Focus on Viscoelasticity
- PMID: 37367140
- PMCID: PMC10298452
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9060469
Rheological Considerations of Pharmaceutical Formulations: Focus on Viscoelasticity
Abstract
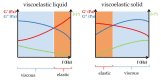
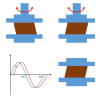
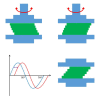
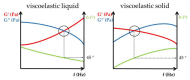
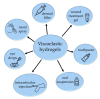
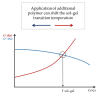
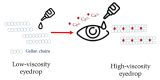
Controlling rheological properties offers the opportunity to gain insight into the physical characteristics, structure, stability and drug release rate of formulations. To better understand the physical properties of hydrogels, not only rotational but also oscillatory experiments should be performed. Viscoelastic properties, including elastic and viscous properties, are measured using oscillatory rheology. The gel strength and elasticity of hydrogels are of great importance for pharmaceutical development as the application of viscoelastic preparations has considerably expanded in recent decades. Viscosupplementation, ophthalmic surgery and tissue engineering are just a few examples from the wide range of possible applications of viscoelastic hydrogels. Hyaluronic acid, alginate, gellan gum, pectin and chitosan are remarkable representatives of gelling agents that attract great attention applied in biomedical fields. This review provides a brief summary of rheological properties, highlighting the viscoelasticity of hydrogels with great potential in biomedicine.
Keywords: biomedicine; elastic and viscous moduli; oscillatory rheology; viscoelastic gel; viscosity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
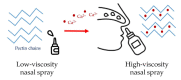
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

