Comparative Electrokinetic Study of Alginate-Coated Colloidal Particles
- PMID: 37367163
- PMCID: PMC10297717
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9060493
Comparative Electrokinetic Study of Alginate-Coated Colloidal Particles
Abstract
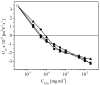
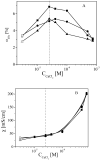
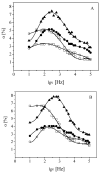
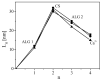
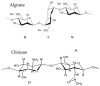
Alginates are a family of natural polysaccharides with promising potential in biomedical applications and tissue regeneration. The design of versatile alginate-based structures or hydrogels and their stability and functionality depend on the polymer's physicochemical characteristics. The main features of alginate chains that determine their bioactive properties are the molar ratio of mannuronic and glucuronic residues (M/G ratio) and their distribution along the polymer chain (MM-, GG-, and MG blocks). The present study is focused on investigating the influence of the physicochemical characteristics of alginate (sodium salt) on the electrical properties and stability of the dispersion of polymer-coated colloidal particles. Ultrapure and well-characterized biomedical-grade alginate samples were used in the investigation. The dynamics of counterion charge near the vicinity of adsorbed polyion is studied via electrokinetic spectroscopy. The results show that the experimental values of the frequency of relaxation of the electro-optical effect are higher compared to the theoretical ones. Therefore, it was supposed that polarization of the condensed Na+ counterions occurs at specific distances according to the molecular structure (G-, M-, or MG-blocks). In the presence of Ca2+, the electro-optical behavior of the particles with adsorbed alginate molecules almost does not depend on the polymer characteristics but was affected by the presence of divalent ions in the polymer layer.
Keywords: adsorption; alginate; colloidal particles; cross-linking; electrokinetic spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Polysaccharide/Carbon Quantum Dots Composite Film on Model Colloidal Particles-An Electro-Optical Study.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Sep 14;15(18):3766. doi: 10.3390/polym15183766. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765620 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Dynamics of Alginate Gels Cross-Linked by Polyvalent Ions Probed via Solid State NMR Spectroscopy.Biomacromolecules. 2017 Aug 14;18(8):2478-2488. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00627. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Biomacromolecules. 2017. PMID: 28636347
-
Counterion release from adsorbed highly charged polyelectrolyte: an electrooptical study.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2006 Jun 15;298(2):550-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2006.01.020. Epub 2006 Feb 14. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2006. PMID: 16480999
-
Alginate-Based Hydrogels and Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications.Mar Drugs. 2023 Mar 13;21(3):177. doi: 10.3390/md21030177. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36976226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of polyelectrolyte adsorption and colloidal flocculation upon mixing studied using mono-dispersed polystyrene latex particles.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2015 Dec;226(Pt A):101-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2015.09.004. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2015. PMID: 26456137 Review.
Cited by
-
Polysaccharide/Carbon Quantum Dots Composite Film on Model Colloidal Particles-An Electro-Optical Study.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Sep 14;15(18):3766. doi: 10.3390/polym15183766. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haug A., Smidsrod O., Larsen B., Gronowitz S., Hoffman R.A., Westerdahl A. The Effect of Divalent Metals on the Properties of Alginate Solutions. II. Comparison of Different Metal Ions. Acta Chem. Scand. 1965;19:341–351. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.19-0341. - DOI
-
- Sahoo D.R., Biswal T. Alginate and its application to tissue engineering. SN Appl. Sci. 2021;3:30–35. doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-04096-w. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

