Application of Red Onion Peel Extract for Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Hydrogels Exhibiting Antimicrobial Properties
- PMID: 37367169
- PMCID: PMC10298306
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9060498
Application of Red Onion Peel Extract for Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Hydrogels Exhibiting Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
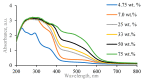
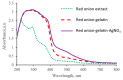
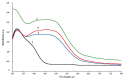
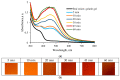
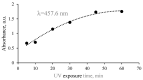
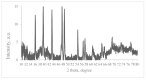
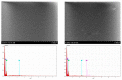
UV-initiated green synthesis of metal nanoparticles by using plant extracts as photoreducing agents is of particular interest since it is an environmentally friendly, easy-to-maintain, and cost-effective method. Plant molecules that act as reducing agents are assembled in a highly controlled way which makes them suitable for metal nanoparticle synthesis. Depending on the plant species, their application for green synthesis of metal nanoparticles for diverse applications may contribute to the mediation/reduction in organic waste amounts, thus enabling the implementation of the circular economy concept. In this work, UV-initiated green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles in hydrogels and hydrogel's thin films containing gelatin (matrix), red onion peel extract of different concentrations, water, and a small amount of 1 M AgNO3 have been investigated and characterized using UV-Vis spectroscopy, SEM and EDS analysis, XRD technique, performing swelling experiments and antimicrobial tests using bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa), yeasts (Candida parapsilosis, Candida albicans) and microscopic fungi (Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus fumigatus). It was found that the antimicrobial effectiveness of the silver-enriched red onion peel extract-gelatin films was higher at lower AgNO3 concentrations as compared to those usually used in the commercially available antimicrobial products. The enhancement of the antimicrobial effectiveness was analyzed and discussed, assuming the synergy between photoreducing agent (red onion peel extract) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) in the initial gel solutions leading to the intensification of Ag nanoparticles production.
Keywords: Ag NPs; UV-Vis spectrophotometry; antimicrobial activity; gels; green synthesis; red onion peel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jaiswal N., Rizvi S.I. Variation of Antioxidant Capacity in Different Layers of Onion (Allium cepa L.) at Two Different Stages of Maturation. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012;8:126–130. doi: 10.2174/157340112800840763. - DOI
-
- Robards K., Antolovich M. Analytical chemistry of frit bioflavonoids—A review. Analyst. 1997;122:11R–34R. doi: 10.1039/a606499j. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

