Pressure Analysis in Rigid and Flexible Real Arteriovenous Fistula with Thickness Variation In Vitro
- PMID: 37367274
- PMCID: PMC10299082
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb14060310
Pressure Analysis in Rigid and Flexible Real Arteriovenous Fistula with Thickness Variation In Vitro
Abstract
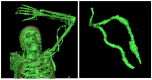
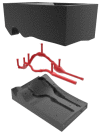
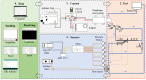
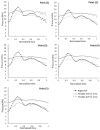
An arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is the access most recommended by several authors. However, its manufacture and use can cause several problems in the short, medium and long term. The study of fluid dynamics related to the structure of the AVF can provide information necessary for the reduction of these problems and a better quality of life for patients. The present study analyzed pressure variation in a rigid and flexible (thickness variation) model of AVFs manufactured based on patient data. A computed tomography was performed from which the geometry of the AVF was removed. This was treated and adapted to the pulsatile flow bench. Bench tests with simulation of systolic-diastolic pulse showed higher pressure peaks in the rigid AVF followed by the flexible model with 1 mm thickness. The inflection of the pressure values of the flexible AVF in relation to the rigid one was observed, being more expressive in the flexible AVF of 1 mm. The 1 mm flexible AVF presented an average pressure close to the physiological one and a smaller pressure drop, showing that this AVF model presents the best condition among the three to serve as a basis for the development of an AVF substitute.
Keywords: arteriovenous fistula; flexible; pressure pulse; rigid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Types of Arteriovenous Fistulas. [(accessed on 19 July 2022)]; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493195/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

