The Landscape of the DNA Transposons in the Genome of the Horezu_LaPeri Strain of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 37367310
- PMCID: PMC10299278
- DOI: 10.3390/insects14060494
The Landscape of the DNA Transposons in the Genome of the Horezu_LaPeri Strain of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
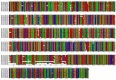
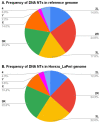
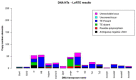
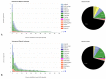
Natural transposons (NTs) represent mobile DNA sequences found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. Drosophila melanogaster (the fruit fly) is a eukaryotic model organism with NTs standing for about 20% of its genome and has contributed significantly to the understanding of various aspects of transposon biology. Our study describes an accurate approach designed to map class II transposons (DNA transposons) in the genome of the Horezu_LaPeri fruit fly strain, consecutive to Oxford Nanopore Technology sequencing. A whole genome bioinformatics analysis was conducted using Genome ARTIST_v2, LoRTE and RepeatMasker tools to identify DNA transposons insertions. Then, a gene ontology enrichment analysis was performed in order to evaluate the potential adaptive role of some DNA transposons insertions. Herein, we describe DNA transposon insertions specific for the Horezu_LaPeri genome and a predictive functional analysis of some insertional alleles. The PCR validation of P-element insertions specific for this fruit fly strain, along with a putative consensus sequence for the KP element, is also reported. Overall, the genome of the Horezu_LaPeri strain contains several insertions of DNA transposons associated with genes known to be involved in adaptive processes. For some of these genes, insertional alleles obtained via mobilization of the artificial transposons were previously reported. This is a very alluring aspect, as it suggests that insertional mutagenesis experiments conducting adaptive predictions for laboratory strains may be confirmed by mirroring insertions which are expected to be found at least in some natural fruit fly strains.
Keywords: DNA natural transposons; Drosophila melanogaster; P-element; bioinformatics; heterochromatin; transposable elements; transposon annotation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kaminker J.S., Bergman C.M., Kronmiller B., Carlson J., Svirskas R., Patel S., Frise E., Wheeler D.A., Lewis S.E., Rubin G.M., et al. The transposable elements of the Drosophila melanogaster euchromatin: A genomics perspective. Genome Biol. 2002;3:RESEARCH0084. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-12-research0084. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

