Effects of Finerenone on Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Diseases: A New Weapon against Cardiorenal Morbidity and Mortality-A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 37367401
- PMCID: PMC10299623
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd10060236
Effects of Finerenone on Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Diseases: A New Weapon against Cardiorenal Morbidity and Mortality-A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
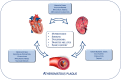
Patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) show high rates of cardiorenal outcomes. In addition, the progression towards renal failure and cardiovascular events rises as CKD worsens. Several studies suggest that the activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) induces cardiac and renal injury, including inflammation and fibrosis. Finerenone is a novel, nonsteroidal, selective MR antagonist (MRA) which has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects in pre-clinical studies. Moreover, two large trials (FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD) investigated the renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with mild to severe CKD in type 2 diabetes which received finerenone. On these bases, this comprehensive review aims to summarize the current knowledge regarding finerenone and its effects on CKD and the cardiovascular system, emphasizing its role in modifying cardiorenal outcomes.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; chronic kidney disease; finerenone; mineralocorticoid receptor; mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ter Maaten J.M., Damman K., Verhaar M.C., Paulus W.J., Duncker D.J., Cheng C., van Heerebeek L., Hillege H.L., Lam C.S.P., Navis G., et al. Connecting heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and renal dysfunction: The role of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016;18:588–598. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.497. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manjunath G., Tighiouart H., Ibrahim H., MacLeod B., Salem D.N., Griffith J.L., Coresh J., Levey A.S., Sarnak M.J. Level of kidney function as a risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular outcomes in the community. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003;41:47–55. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(02)02663-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources