Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saussurea costus as Therapeutic Agents against a Diabetic Rat Model-Approaches to Investigate Pharmacophore Modeling of Human IkB Kinase and Molecular Interaction with Dehydrocostus Lactone of Saussurea costus
- PMID: 37367922
- PMCID: PMC10302201
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo13060764
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saussurea costus as Therapeutic Agents against a Diabetic Rat Model-Approaches to Investigate Pharmacophore Modeling of Human IkB Kinase and Molecular Interaction with Dehydrocostus Lactone of Saussurea costus
Abstract
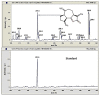
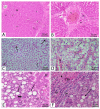
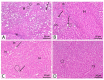
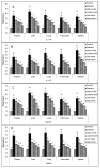
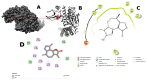
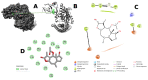
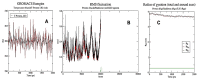
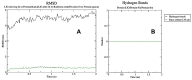
Lactic acid bacteria is well-known as a vital strategy to alleviate or prevent diabetes. Similarly, the plant Saussurea costus (Falc) Lipsch is a preventive power against diabetes. Here, we aimed to determine whether lactic acid bacteria or Saussurea costus is more effective in treating a diabetic rat model in a comparative study manner. An in vivo experiment was conducted to test the therapeutic activity of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (MW719476.1) and S. costus plants against an alloxan-induced diabetic rat model. Molecular, biochemical, and histological analyses were investigated to evaluate the therapeutic characteristics of different treatments. The high dose of S. costus revealed the best downregulated expression for the IKBKB, IKBKG, NfkB1, IL-17A, IL-6, IL-17F, IL-1β, TNF-α, TRAF6, and MAPK genes compared to Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and the control groups. The downregulation of IKBKB by S. costus could be attributed to dehydrocostus lactone as an active compound with proposed antidiabetic activity. So, we performed another pharmacophore modeling analysis to test the possible interaction between human IkB kinase beta protein and dehydrocostus lactone as an antidiabetic drug. Molecular docking and MD simulation data confirmed the interaction between human IkB kinase beta protein and dehydrocostus lactone as a possible drug. The target genes are important in regulating type 2 diabetes mellitus signaling, lipid and atherosclerosis signaling, NF-κB signaling, and IL-17 signaling pathways. In conclusion, the S. costus plant could be a promising source of novel therapeutic agents for treating diabetes and its complications. Dehydrocostus lactone caused the ameliorative effect of S. costus by its interaction with human IkB kinase beta protein. Further, future studies could be conducted to find the clinical efficacy of dehydrocostus lactone.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene; Lactiplantibacillus plantarum; Saussurea costus; biochemical; diabetes mellitus; docking; histological analysis; pharmacophore modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





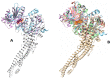
References
-
- Davies M.J., D’Alessio D.A., Fradkin J., Kernan W.N., Mathieu C., Mingrone G., Buse J.B. Management of Hyperglycaemia in Type 2 Diabetes. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Diabetologia. 2022;65:1925–1966. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05787-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mammate N., El Oumari F.E., Imtara H., Belchkar S., Lahrichi A., Alqahtani A.S., Houssaini T.S. Antioxidant and Anti-Urolithiatic Activity of Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts from Saussurea costus (Falc) Lispich Using Scanning Electron Microscopy. Life. 2022;12:1026. doi: 10.3390/life12071026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumar A., Sharma B. Biomedical implications of plant-based principles as antidepressants: Prospects for novel drug development. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2022;22:904–926. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

